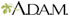Spine anatomy
Description
Before you read about causes of back pain and how it is treated, it may help to understand the anatomy of your spine. This includes the bones, nerves, disks, muscles, and other tissues in and around your spine. If you have back pain, the cause is usually from a problem with a part of your spine anatomy.
The spinal column
The spine is a column of small bones that are called vertebrae. These bones run down the center of your neck and back. They support your upper body and protect your spinal cord.
The spinal column is grouped into different regions by where they are located. The 4 regions of the spinal column are:
- Cervical: These 7 vertebrae support the neck.
- Thoracic: These 12 vertebrae are attached to the ribs in the chest.
- Lumbar: These 5 vertebrae are the lowest and largest bones of the spinal column.
- The sacrum: A bone that is shaped like a shield, connects your back to your pelvis below the spinal column.
The lumbar vertebrae bear more of your body's weight than any other part of your back. Most of your back motion comes from this region. That is why the lumbar region (lower back) is the most likely to get injured.
Each vertebra is referred to by a letter and a number. The letter is the region (C = cervical, T = thoracic, and L = lumbar), and the number indicates the vertebra within that region. For example, C4 is the fourth bone down in the cervical region, and T8 is the eighth bone in the thoracic region.
You may hear your health care provider say after an exam of your spine that "your pain is between L3 and L5." After an MRI scan (an imaging test), your provider may identify the precise location and type of problem. For example, "you have a slipped disk between L4 and L5."
Facet joints are where 2 different vertebrae that are next to each other form a joint. This joint allows the spine to move, especially to twist and bend. They are at the back of the spinal column and one on each side.
Spinal cord and nerve roots
The nerves that connect the brain to the rest of your body run down your back. They form your spinal cord.
Nerve roots are large nerves that branch out from the spinal cord and go out of your spinal column between each vertebra. One nerve root goes out on the right side and the other goes out on the left side. Pressure or injury to these nerves can cause pain, weakness, numbness in your back.
The disks
The spinal bones and vertebrae are separated by disks. These disks cushion your spinal column and maintain the space between each vertebra. It keeps your spinal column mobile and flexible.
The outside of the disk is made mostly of cartilage, which is a strong, flexible tissue. The inside of the disk is a jelly-like substance that contains a lot of water. As you get older, the disk will dry up and lose its ability to act as a good shock absorber.
Ligaments and muscles
The vertebrae and disks of your spine are surrounded by many muscles and ligaments. These provide strength and support when you move, lift, and bend. These tissues are often called soft-tissues because they are not hard, like bone.
Stomach, neck, and chest muscles also support your back. When these muscles are strong and in good condition, they help reduce the stress on your lower back by carrying some of your body weight.
Injury to the muscles and other soft tissues around your spine is a more common cause of back pain than injury to other parts of your spine.
Reviewed By: C. Benjamin Ma, MD, Professor, Chief, Sports Medicine and Shoulder Service, UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, San Francisco, CA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. © 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.