Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) injury - aftercare
Cruciate ligament injury - aftercare; PCL injury - aftercare; Knee injury - posterior cruciate ligament
Images
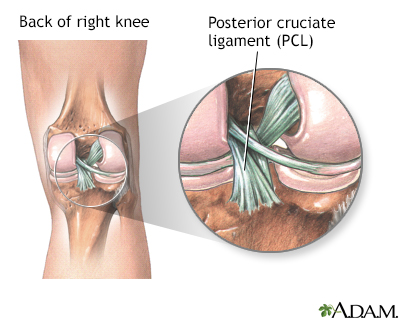
Description
A ligament is a band of tissue that connects a bone to another bone. The posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) is located inside your knee joint and connects the bones of your upper and lower leg.
A PCL injury occurs when the ligament is stretched or torn. A partial PCL tear occurs when only part of the ligament is torn. A complete PCL tear occurs when the entire ligament is torn into two pieces or detaches from the bone.
More About Your Injury
The PCL is one of several ligaments that keep your knee stable. The PCL helps keep your leg bones in place and allows your knee to move back and forth. It is the strongest ligament in the knee. PCL tears often occur as a result of a severe knee injury.
Injuring the PCL takes a lot of force. It can occur if you:
- Get hit very hard on the front of your knee, such as hitting your knee on the dashboard during a car accident
- Fall hard on a bent knee
- Bend the knee too far backward (hyperflexion)
- Land the wrong way after jumping
- Dislocate your entire knee joint
PCL injuries commonly occur with other knee ligament and meniscus damage, including injuries to the nerves and blood vessels. These are usually a result of serious knee trauma and should be seen by a specialist promptly. Skiers and people who play basketball, football, or soccer are more likely to have this type of injury.
What to Expect
With a PCL injury, you may have:
- Mild pain that may get worse over time
- A feeling that your knee is unstable and can shift as if it "gives way"
- Knee swelling that starts right after the injury
- Knee stiffness due to swelling
- Difficulty walking and going down stairs
After examining your knee, your health care provider may order these imaging tests:
- X-rays to check for damage to the bones in your knee.
- An MRI of the knee. An MRI machine takes special pictures of the tissues inside your knee. The pictures will show whether these tissues have been stretched or torn.
- A CT scan or an arteriogram to look for any injuries to your blood vessels.
If you have a PCL injury, you may need:
- Crutches to walk until the swelling and pain get better
- A brace to support and stabilize your knee
- Physical therapy to help improve joint motion and leg strength
- Surgery to rebuild the PCL and possibly other tissues in the knee
If you have a severe injury, such as a knee dislocation when more than one ligament is torn, you will need knee surgery to repair the joint. For milder injuries, you may not need surgery. A lot of people can live and function normally with a torn PCL. However, if you are younger, having a torn PCL and instability of your knee may lead to arthritis as you age. Talk with your provider about the best treatment for you.
Self-care at Home
Follow R.I.C.E. to help reduce pain and swelling:
- Rest your leg and avoid putting weight on it.
- Ice your knee for 20 minutes at a time, 3 to 4 times a day. Do not apply ice directly to your skin. Wrap the ice in a clean cloth first.
- Compress the area by wrapping it with an elastic bandage or compression wrap.
- Elevate your leg by raising it above the level of your heart.
You can use ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) or naproxen (Aleve, Naprosyn) to reduce pain and swelling. Acetaminophen (Tylenol) helps with pain, but not swelling. You can buy these pain medicines at the store.
- Talk with your provider before using these medicines if you have heart disease, high blood pressure, kidney disease, or have had stomach ulcers or internal bleeding in the past.
- Do not take more than the amount recommended on the bottle or by your provider.
Activity
If you have surgery to repair (reconstruct) your PCL:
- You will need physical therapy to regain the full use of your knee.
- Your recovery can take at least 6 months.
If you do not have surgery to repair (reconstruct) your PCL:
- You will need to work with a physical therapist to lessen swelling and pain and regain enough strength in your leg to resume activity.
- Your knee will likely be placed in a brace and may have restricted motion.
- Your recovery may take a few months.
When to Call the Doctor
Contact your provider if:
- You have an increase in swelling or pain
- Self-care does not seem to help
- You lose feeling in your foot
- Your foot or leg feels cold or changes color
If you have surgery, contact your surgeon if you have:
- A fever of 100°F (38°C) or higher
- Drainage from the incisions
- Bleeding that won't stop
References
Petrigliano FA, Vellios EE, Montgomery SR, Johnson JS, McAllister DR. Posterior cruciate ligament injuries. In: Miller MD, Thompson SR, eds. DeLee, Drez, & Miller's Orthopaedic Sports Medicine. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 100.
Sheng A, Splittgerber L. Posterior cruciate ligament sprain. In: Frontera WR, Silver JK, Rizzo TD Jr, eds. Essentials of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 76.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 4/24/2023
Reviewed By: C. Benjamin Ma, MD, Professor, Chief, Sports Medicine and Shoulder Service, UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, San Francisco, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2024 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
