Managing tension headaches at home
Tension-type headache - self-care; Muscle contraction headache - self-care; Headache - benign - self-care; Headache - tension- self-care; Chronic headaches - tension - self-care; Rebound headaches - tension - self-care
Images
Description
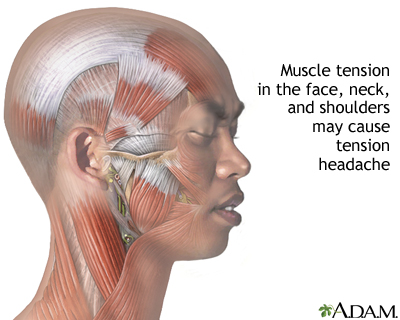
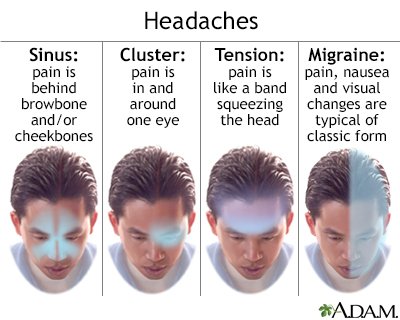
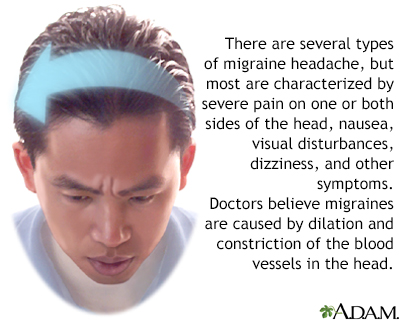
A tension headache is pain or discomfort in your head, scalp, or neck. Tension headache is a common type of headache. It can occur at any age, but it is most common in teens and adults.
A tension headache occurs when neck and scalp muscles become tense or contract. The muscle contractions can be a response to stress, depression, a head injury, or anxiety.
When You Have a Tension Headache
Hot or cold showers or baths may relieve a headache for some people. You may also want to rest in a quiet room with a cool cloth on your forehead.
Gently massaging your head and neck muscles may provide relief.
If your headaches are due to stress or anxiety, you may want to learn ways to relax.
Over-the-counter pain medicine, such as aspirin, ibuprofen, or acetaminophen, may relieve pain. If you are planning to take part in an activity that you know will trigger a headache, taking pain medicine beforehand may help.
Avoid smoking and drinking alcohol.
Follow your health care provider's instructions about how to take your medicines. Rebound headaches are headaches that keep coming back. They can occur from overuse of pain medicine. If you take pain medicine more than 3 days a week on a regular basis, you can develop rebound headaches.
Be aware that aspirin and ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) can irritate your stomach. If you take acetaminophen (Tylenol), DO NOT take more than a total of 4,000 mg (4 grams) of regular strength or 3,000 mg (3 grams) of extra strength a day to avoid liver damage.
Preventing Tension Headaches
Knowing your headache triggers can help you avoid situations that cause your headaches. A headache diary can help. When you get a headache, write down the following:
- Day and time the pain began
- What you ate and drank over the past 24 hours
- How much you slept
- What you were doing and where you were right before the pain started
- How long the headache lasted and what made it stop
Review your diary with your provider to identify triggers or a pattern to your headaches. This can help you and your provider create a treatment plan. Knowing your triggers can help you avoid them.
Lifestyle changes that may help include:
- Use a different pillow or change sleeping positions.
- Practice good posture when reading, working, or doing other activities.
- Exercise and stretch your back, neck, and shoulders often when typing, working on computers, or doing other close-up work.
- Get more vigorous exercise. This is an exercise that gets your heart beating fast. (Check with your provider about what kind of exercise is best for you.)
- Have your eyes checked. If you have glasses, use them.
- Learn and practice stress management. Some people find relaxation exercises or meditation helpful.
If your provider prescribes medicines to prevent headaches or help with stress, follow instructions exactly on how to take them. Tell your provider about any side effects.
When to Call the Doctor
Call 911 or the local emergency number if:
- You are experiencing "the worst headache of your life."
- You have speech, vision, or movement problems or loss of balance, especially if you have not had these symptoms with a headache before.
- You have a fever with your headache.
- A headache starts suddenly.
Schedule an appointment or call your provider if:
- Your headache pattern or pain changes.
- Treatments that once worked no longer help.
- You have side effects from your medicine.
- You are pregnant or could become pregnant. Some medicines should not be taken during pregnancy.
- You need to take pain medicines more than 3 days a week.
- Your headaches are more severe when lying down.
References
Garza I, Whealy MA, Robertson CE, Smith JH. Headache and other craniofacial pain. In: Daroff RB, Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, eds. Bradley's and Daroff's Neurology in Clinical Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 102.
Jensen RH. Tension-type headache - the normal and most prevalent headache. Headache. 2018;58(2):339-345. PMID: 28295304 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28295304/.
Rozental JM. Tension-type headache, chronic tension-type headache, and other chronic headache types. In: Benzon HT, Raja SN, Liu SS, Fishman SM, Cohen SP, eds. Essentials of Pain Medicine. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 20.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 11/9/2021
Reviewed By: Joseph V. Campellone, MD, Department of Neurology, Cooper Medical School at Rowan University, Camden, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2024 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
