Preventing pressure ulcers
Decubitus ulcer prevention; Bedsore prevention; Pressure sores prevention
Images
I Would Like to Learn About:
Description
Pressure ulcers are also called bedsores, or pressure sores. They can form when your skin and soft tissue press against a harder surface, such as a chair or bed, for a prolonged time. This pressure reduces blood supply to that area. Lack of blood supply can cause the skin tissue in this area to become damaged or die. When this happens, a pressure ulcer may form.
You have a risk of developing a pressure ulcer if you:
- Spend most of your day in a bed or a chair with minimal movement
- Are overweight or underweight
- Are not able to control your bowels or bladder or have leakage of urine or stool
- Have decreased feeling in an area of your body
- Spend a lot of time in one position
You will need to take steps to prevent these problems.
Self-care
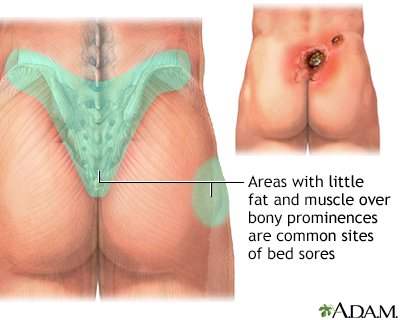
You, or your caregiver, need to check your body every day from head to toe. Pay special attention to the areas where pressure ulcers often form. These areas are the:
- Heels and ankles
- Knees
- Hips
- Spine
- Tailbone area
- Elbows
- Shoulders and shoulder blades
- Back of the head
- Ears
Contact your health care provider if you see early signs of pressure ulcers. These signs are:
- Skin redness
- Warm areas
- Spongy or hard skin
- Breakdown of the top layers of skin or a sore
Treat your skin gently to help prevent pressure ulcers.
- When washing, use a soft sponge or cloth. Do not scrub hard.
- Use moisturizing cream and skin protectants on your skin every day or more as directed by your provider.
- Clean and dry areas underneath your breasts and in your groin.
- Do not use talc powder or strong soaps.
- Try not to take a bath or shower every day. It can dry out your skin more.
Eat enough calories and protein to stay healthy.
Drink plenty of water every day.
Make sure your clothes are not increasing your risk of developing pressure ulcers:
- Avoid clothes that have thick seams, buttons, or zippers that press on your skin.
- Do not wear clothes that are too tight.
- Keep your clothes from bunching up or wrinkling in areas where there is any pressure on your body.
After urinating or having a bowel movement:
- Clean the area right away. Dry well.
- Ask your provider about creams or other medicines to help protect your skin in this area.
If You Use a Wheelchair
Make sure your wheelchair is the right size for you.
- Have your provider or physical therapist check the fit once or twice a year.
- If you gain weight, ask your provider or physical therapist to check how you fit your wheelchair.
- If you feel pressure anywhere, have your provider or physical therapist check your wheelchair.
Sit on a foam or gel seat cushion that fits your wheelchair. Natural sheepskin pads are also helpful to reduce pressure on the skin. Do not sit on a donut-shaped cushions.
You or your caregiver should shift your weight in your wheelchair every 15 to 20 minutes. This will take pressure off certain areas and maintain blood flow:
- Lean forward
- Lean to one side, then lean to the other side
If you transfer yourself (move to or from your wheelchair), lift your body up with your arms. Do not drag yourself. If you are having trouble transferring into your wheelchair, ask a physical therapist to teach you the proper technique.
If your caregiver transfers you, make sure they know the proper way to move you.
When You Are in Bed
Use a foam mattress or one that is filled with gel or air. Place pads under your bottom to absorb wetness to help keep your skin dry.
Use a soft pillow or a piece of soft foam between parts of your body that press against each other or against your mattress.
When you are lying on your side, put a pillow or foam between your knees and ankles.
When you are lying on your back, put a pillow or foam:
- Under your heels. Or, place a pillow under your calves to lift up your heels, as another way to relieve pressure on your heels.
- Under your tailbone area.
- Under your shoulders and shoulder blades.
- Under your elbows.
Other tips are:
- Do not put pillows under your knees. It puts pressure on your heels.
- Never drag yourself to change your position or get in or out of bed. Dragging causes skin breakdown. Get help if you need moving in bed or getting in or out of bed.
- If someone else moves you, they should lift you or use a draw sheet (a special sheet used for this purpose) to move you.
- Change your position every 1 to 2 hours to keep the pressure off any one spot.
- Sheets and clothing should be dry and smooth, with no wrinkles.
- Remove any objects such as pins, pencils or pens, or coins from your bed.
- Do not raise the head of your bed to more than a 30 degree angle. Being flatter keeps your body from sliding down. Sliding may harm your skin.
- Check your skin often for any areas of skin breakdown.
When to Call the Doctor
Contact your provider right away if:
- You notice a sore, redness, or any other change in your skin that last for more than a few days or becomes painful, warm, or begins to drain pus.
- Your wheelchair does not fit.
Talk to your provider if you have questions about pressure ulcers and how to prevent them.
Related Information
Skin graftMultiple sclerosis
Neurogenic bladder
Spinal cord trauma
Bowel incontinence
Skin care and incontinence
Recovering after stroke
Eating extra calories when sick - adults
Caring for muscle spasticity or spasms
Multiple sclerosis - discharge
Stroke - discharge
Pressure ulcers - what to ask your doctor
References
James WD, Elston DM, Treat JR, Rosenbach MA, Neuhaus IM. Dermatoses resulting from physical factors. In: James WD, Elston DM, Treat JR, Rosenbach MA, Neuhaus IM eds. Andrews' Diseases of the Skin. 13th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 3.
Qaseem A, Humphrey LL, Forciea MA, Starkey M, Denberg TD. Clinical Guidelines Committee of the American College of Physicians. Treatment of pressure ulcers: a clinical practice guideline from the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2015;162(5):370-379. PMID: 25732279 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25732279/.
Woelfel SL, Armstrong DG, Shin L. Wound care. In: Sidawy AN, Perler BA, eds. Rutherford's Vascular Surgery and Endovascular Therapy. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 118.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 5/28/2024
Reviewed By: Ramin Fathi, MD, FAAD, Director, Phoenix Surgical Dermatology Group, Phoenix, AZ. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2025 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
