Colon cancer - series
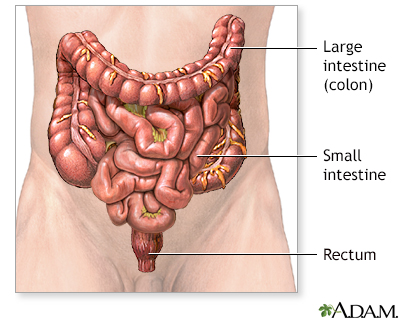
Normal anatomy
The colon, or large intestine, is a muscular tube that begins at the end of the small intestine and ends at the rectum. The colon absorbs water from liquid stool that is delivered to it from the small intestine.
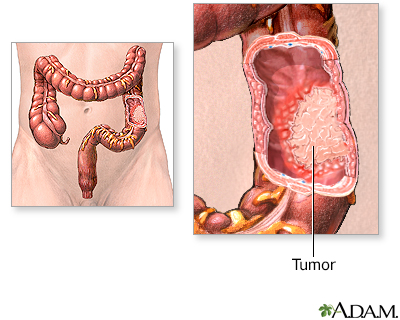
Indication
Colon cancer is the third most common cancer in the United States. Risk factors include a diet low in fiber and high in fat, certain types of colonic polyps, inflammatory bowel disease (such as Crohn disease or ulcerative colitis), and certain hereditary disorders.
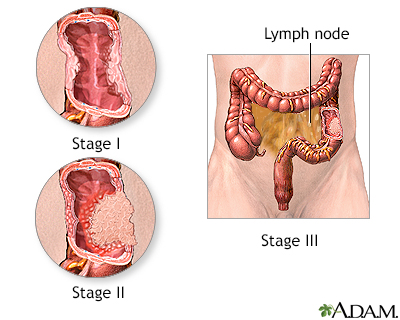
Incision
The treatment of colon cancer depends on the stage of the disease. Stage I cancer is limited to the inner lining of the colon; Stage II cancer involves the entire wall of the colon; Stage III cancer has spread to the lymph nodes; Stage IV cancer has spread to other organs (metastasized).
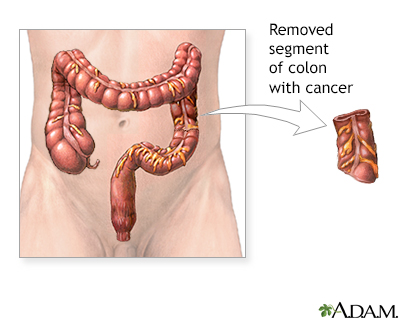
Procedure
Surgery is the main treatment for colon cancer and removal of the involved colon is required. If the cancer is located near the rectum, a colostomy may be necessary. For stage I and II colon cancer, surgery is usually the only treatment. For stage III or IV colon cancer, chemotherapy is necessary after surgery. There is also some suggestion that chemotherapy may also be helpful in some selected stage II patients. Chemotherapy involves a course of drugs which are toxic to cancer cells.
Aftercare
Stage I and II colon cancer have very high cure rates (60% to 90%); lower cure rates are seen with stage III and IV colon cancer. To detect colon cancer early, when it is most curable, everyone over the age of 55 should have bi-annual endoscopic examinations of the colon.
Related Information
Colorectal cancerBACK TO TOP
Review Date: 4/18/2023
Reviewed By: John Roberts, MD, Professor of Internal Medicine (Medical Oncology), Yale Cancer Center, New Haven, CT. He is board certified in Internal Medicine, Medical Oncology, Pediatrics, Hospice and Palliative Medicine. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2024 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
