Anal fissure - series
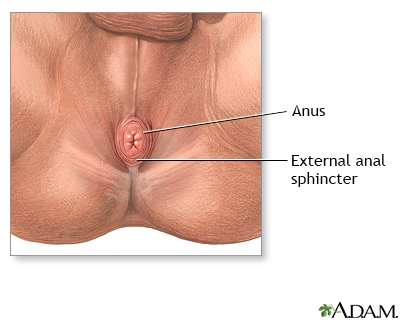
Normal anatomy
The anus is a sphincter at the end of the rectum through which passes stool during defecation. The anal sphincter is a critical mechanism for control of fecal continence.
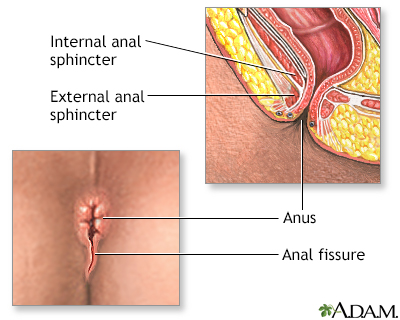
Indication
Anal fissures are tears in the skin overlying the anal sphincter, usually due to increased tone of the anal sphincter muscles, and a failure of these muscle to relax. Anal fissures cause pain during defecation and bleeding from the anus.
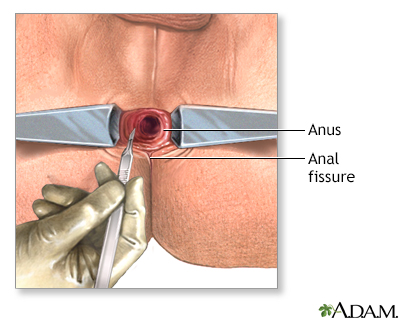
Incision
Most anal fissures can be treated successfully with conservative measures, which include stool softeners and warm soaks. The goal is to relax the anal sphincter, which allows the fissure to heal. If these methods are ineffective, surgery is necessary. This is called an internal sphincterotomy, a procedure in which the anal sphincter is partially cut, thus allowing it to relax and permitting the fissure to heal.
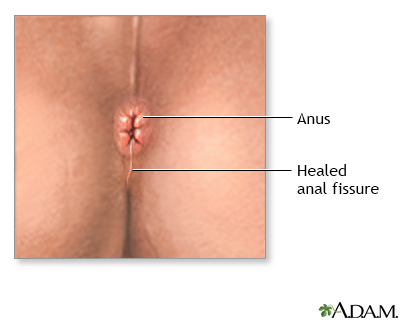
Procedure
Sphincterotomy, when properly performed, is very effective in healing anal fissures.
BACK TO TOP
Review Date: 6/11/2024
Reviewed By: Jenifer K. Lehrer, MD, Department of Gastroenterology, Aria - Jefferson Health Torresdale, Jefferson Digestive Diseases Network, Philadelphia, PA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2025 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
