Abdominal exploration - series
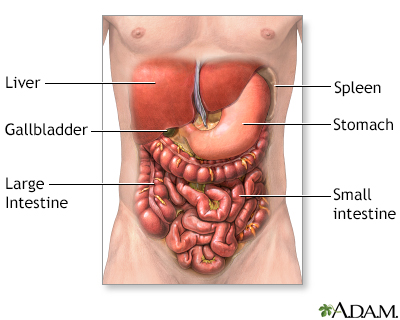
Normal anatomy
The abdomen contains many vital organs: the stomach, the small intestine (jejunum and ileum), the large intestine (colon), the liver, the spleen, the gallbladder, the pancreas, the uterus, the fallopian tubes, the ovaries, the kidneys, the ureters, the bladder, and many blood vessels (arteries and veins).
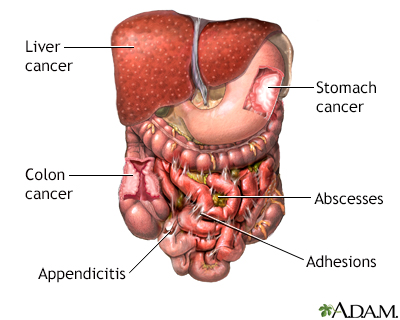
Indication
The surgical exploration of the abdomen, also called an exploratory laparotomy, may be recommended when there is abdominal disease from an unknown cause (to diagnose), or trauma to the abdomen (gunshot or stab-wounds, or "blunt trauma").
Diseases that may be discovered by exploratory laparotomy include:
- Inflammation of the appendix (acute appendicitis)
- Inflammation of the pancreas (acute or chronic pancreatitis)
- Pockets of infection (retroperitoneal abscess, abdominal abscess, pelvic abscess))
- Presence of uterine tissue (endometrium) in the abdomen (endometriosis)
- Inflammation of the Fallopian tubes (salpingitis)
- Scar tissue in the abdomen (adhesions)
- Cancer (of the ovary, colon, pancreas, liver)
- Inflammation of an intestinal pocket (diverticulitis)
- Hole in the intestine (intestinal perforation)
- Pregnancy in the abdomen instead of uterus (ectopic pregnancy)
- To determine the extent of certain cancers (Hodgkin's lymphoma)
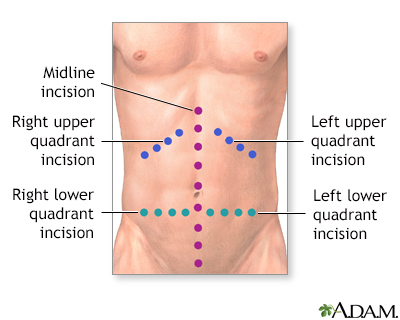
Procedure
While the patient is deep asleep and pain-free (general anesthesia), the surgeon makes an incision into the abdomen and examines the abdominal organs. Different incisions are sometimes used depending on the circumstance. Common incisions include a vertical midline incision, and right or left upper or lower quadrant transverse incisions. Tissue samples (biopsies) can be taken and diseased areas can be evaluated. When the treatment is complete, the incision is closed with either sutures or skin staples.
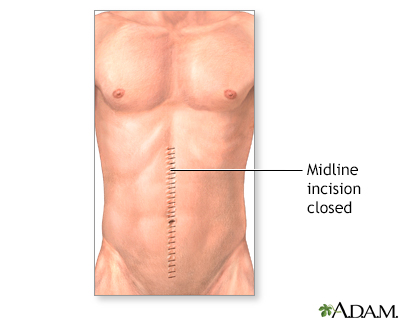
Aftercare
The outcome from surgery varies with the disease process, as does the course and duration of recovery. Exploratory laparotomy is most commonly performed for trauma, severe abdominal pain of unknown cause, intestinal obstruction, inflammatory diseases like appendicitis and diverticulitis, and cancer of any of the abdominal organs.
BACK TO TOP
Review Date: 2/28/2022
Reviewed By: Debra G. Wechter, MD, FACS, General Surgery Practice Specializing in Breast Cancer, Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2024 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
