Episiotomy - series
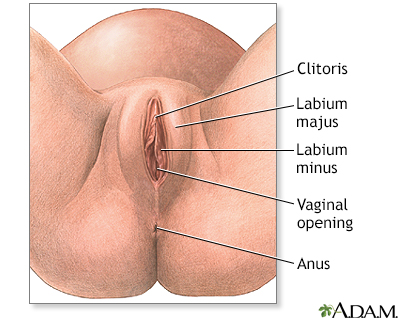
Normal anatomy
The external female genitalia include the labia, the opening to the vaginal canal, and the clitoris. During birth, the vaginal canal expands to let the baby through.
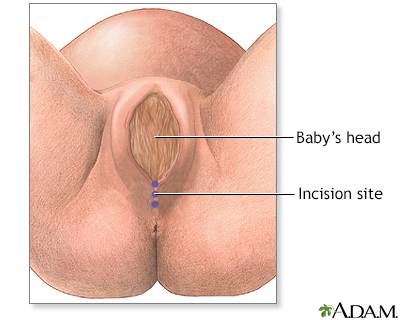
Indication
Although done much less often an episiotomy may be needed if the baby's head is too big for the mother's vaginal opening, or the baby is in a breech position (feet or buttocks coming first) and there is a problem during delivery.
Just before the baby is born and while the woman is awake and pain-free (local anesthesia or epidural block), an incision is made at the bottom of the vaginal opening to enlarge it for the delivery of the baby's head.
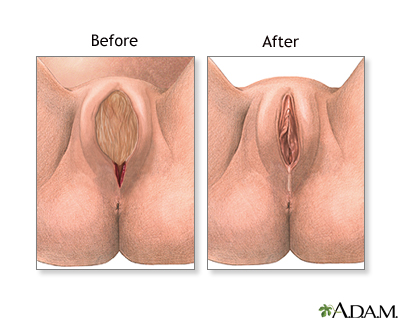
Aftercare
Stitches (sutures) are used to close the incision after both the baby and placenta have been delivered. The stitches are absorbed by the body and do not need to be removed.
BACK TO TOP
Review Date: 4/19/2022
Reviewed By: John D. Jacobson, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Loma Linda University School of Medicine, Loma Linda, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2024 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
