Exercise and immunity
Battling another cough or cold? Feeling tired all the time? You may feel better if you take a daily walk or follow a simple exercise routine a few times a week.
Images



I Would Like to Learn About:
Information
Exercise helps decrease your chances of developing heart disease. It also keeps your bones healthy and strong.
We do not know exactly if or how exercise increases your immunity to certain illnesses. There are several theories. However, none of these theories have been proven. Some of these theories are:
- Physical activity may help flush bacteria out of the lungs and airways. This may reduce your chance of getting a cold, flu, or other illness.
- Exercise causes changes in antibodies and white blood cells (WBCs). WBCs are the body's immune system cells that fight disease. These antibodies or WBCs circulate more rapidly, so they could detect illnesses earlier than they might have before. However, no one knows whether these changes help prevent infections.
- The brief rise in body temperature during and right after exercise may prevent bacteria from growing. This temperature rise may help the body fight infection better. (This is similar to what happens when you have a fever.)
- Exercise slows down the release of stress hormones. Some stress increases the chance of illness. Lower stress hormones may protect against illness.
Exercise is good for you, but, you should not overdo it. People who already exercise should not exercise more just to increase their immunity. Heavy, long-term exercise (such as marathon running and intense gym training) could actually cause harm.
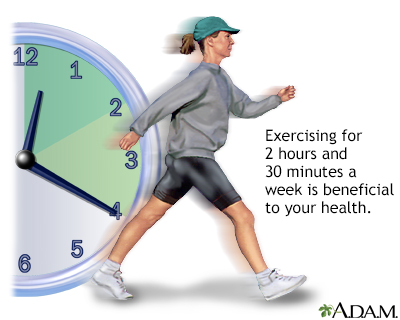
Studies have shown that people who follow a moderately active lifestyle, benefit most from starting (and sticking to) an exercise program. A moderate program can consist of:
- Bicycling with your children a few times a week
- Taking daily 20 to 30 minute walks
- Going to the gym every other day
- Playing golf regularly
Exercise makes you feel healthier and more energetic. It can help you feel better about yourself. So go ahead, take that aerobics class or go for that walk. You will feel better and healthier for it.
There is no strong evidence to prove that taking immune supplements along with exercising lowers the chance of illness or infections.
References
Best TM, Asplund CA. Exercise physiology. In: Miller MD, Thompson SR. eds. DeLee, Drez, & Miller's Orthopaedic Sports Medicine. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 6.
Jiang NM, Abalos KC, Petri WA. Infectious diseases in the athlete. In: Miller MD, Thompson SR. eds. DeLee, Drez, & Miller's Orthopaedic Sports Medicine. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 17.
Lanfranco F, Ghigo E, Strasburger CJ. Hormones and athletic performance. In: Melmed S, Auchus RJ, Goldfine AB, Koenig RJ, Rosen CJ, eds. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 27.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 2/8/2024
Reviewed By: Linda J. Vorvick, MD, Clinical Professor, Department of Family Medicine, UW Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2024 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
