Esophageal manometry
Esophageal motility studies; Esophageal function studies
Esophageal manometry is a test to measure how well the esophagus is working.
Images
How the Test is Performed
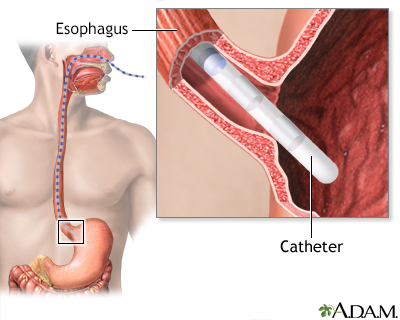
During esophageal manometry, a thin, pressure-sensitive tube is passed through your nose, down the esophagus, and into your stomach. This test is done in a hospital or outpatient center by a specially trained doctor called a gastroenterologist.
Before the procedure, you receive numbing medicine inside the nose. This helps make the insertion of the tube less uncomfortable.
After the tube is in the stomach, the tube is pulled slowly back into your esophagus. At this time, you are asked to swallow. The pressure of the muscle contractions is measured along several sections of the tube.
While the tube is in place, other studies of your esophagus may be done. The tube is removed after the tests are completed. The test takes about 1 hour.
How to Prepare for the Test
You should not have anything to eat or drink for 8 hours before the test. If you have the test in the morning, Do not eat or drink after midnight.
Tell your health care provider about all medicines you are taking. These include vitamins, herbs, and other over-the-counter medicines and supplements.
How the Test will Feel
You may have a gagging sensation and discomfort when the tube passes through your nose and throat. You may also feel discomfort in your nose and throat during the test.
Why the Test is Performed
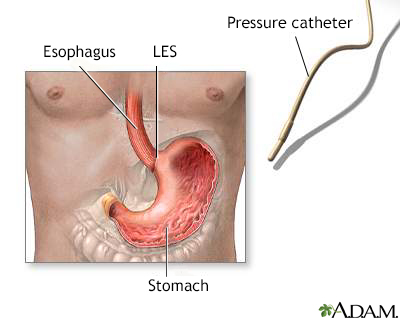
The esophagus is the tube that carries food from your mouth into the stomach. When you swallow, muscles in your esophagus squeeze (contract) to push food toward the stomach. Valves, or sphincters, inside the esophagus open to let food and liquid through. They then close to prevent food, fluids, and stomach acid from moving backward. The sphincter at the bottom of the esophagus is called the lower esophageal sphincter, or LES.
Esophageal manometry is done to see if the esophagus is contracting and relaxing properly. The test helps diagnose swallowing problems. During the test, your doctor can also check the LES to see if it opens and closes properly.
The test may be ordered if you have symptoms of:
- Heartburn or nausea after eating (gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD)
- Problems swallowing (feeling like food is stuck behind the breast bone)
Normal Results
The LES pressure and muscle contractions are normal when you swallow.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Abnormal results may indicate:
- A problem with the esophagus that affects its ability to move food toward the stomach (achalasia)
- A weak LES, which causes heartburn (GERD)
- Abnormal contractions of the esophagus muscles that do not effectively move food to the stomach (esophageal spasm)
Risks
Risks of this test include:
- Slight nosebleed
- Sore throat
- Hole or perforation in the esophagus (this rarely happens)
Related Information
AchalasiaEsophageal spasm
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
References
Pandolfino JE, Kahrilas PJ. Esophageal neuromuscular function and motility disorders. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 44.
Richter JE, Vaezi MF. Gastroesophageal reflux disease. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 46.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 8/7/2023
Reviewed By: Michael M. Phillips, MD, Emeritus Professor of Medicine, The George Washington University School of Medicine, Washington, DC. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2025 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
