Dental x-rays
X-ray - teeth; Radiograph - dental; Bitewings; Periapical film; Panoramic film; Cephalometric x-ray; Digital image
Dental x-rays are a type of image of the teeth and mouth. X-rays are a form of high energy electromagnetic radiation. The x-rays penetrate the body to form an image on film or screen. X-rays can be either digital or developed on a film.
Structures that are dense (such as silver fillings or metal restoration) will block most of the light energy from the x-ray. This makes them appear white in the image. Structures that contain air will be black, and teeth, tissue, and fluid will appear as shades of gray.
Images
I Would Like to Learn About:
How the Test is Performed
The test is performed in the dentist's office. There are many types of dental x-rays. Some of them are:
- Bitewing. Shows the crown portions of the top and bottom teeth together when the person bites on a biting tab.
- Periapical. Shows 1 or 2 complete teeth from crown to root.
- Palatal (also called occlusal). Captures all the upper or lower teeth in one shot while the film rests on the biting surface of the teeth.
- Panoramic. Requires a special machine that rotates around the head. The x-ray captures all of the jaws and teeth in one shot. It is used to plan treatment for dental implants, check for impacted wisdom teeth, and detect jaw problems. A panoramic x-ray is not the best method for detecting cavities, unless the decay is very advanced and deep.
- Cephalometric. Presents the side view of the face and represents relationship of the jaw to each other as well as to the rest of the structures. It is helpful to diagnose any airway problems.
Many dentists take x-rays using digital technology. These images run through a computer. The amount of radiation given off during the procedure is less than traditional methods. Other types of dental x-rays can create a 3-D picture of the jaw. Cone beam computerized tomography (CBCT) may be used before dental surgery, such as when several implants are being placed.
How to Prepare for the Test
There is no special preparation. You need to remove any metal objects in the area of the x-ray exposure. A lead apron may be placed over your body. Tell your dentist if you might be pregnant.
How the Test will Feel
The x-ray itself causes no discomfort. Biting on the piece of film makes some people gag. Slow, deep breathing through the nose usually relieves this feeling. Both CBCT and cephalometric x-ray do not require any biting pieces.
Why the Test is Performed
Dental x-rays help diagnose disease and injury of the teeth and gums as well as help planning the appropriate treatment.
Normal Results
Normal x-rays show a normal number, structure, and position of the teeth and jaw bones. There are no cavities or other problems.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Dental x-rays may be used to identify the following:
- The number, size, and position of teeth
- Partially or fully impacted teeth
- The presence and severity of tooth decay (called cavities or dental caries)
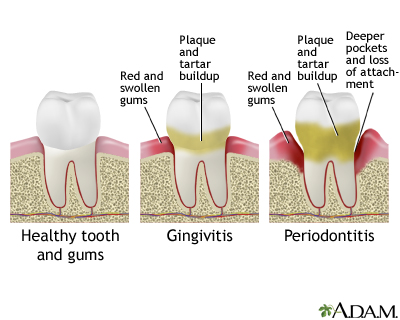
- Bone damage (such as from gum disease called periodontitis)
- Abscessed teeth
- Fractured jaw
- Problems in the way the upper and lower teeth fit together (malocclusion)
- Other abnormalities of the teeth and jaw bones
Risks
There is very low radiation exposure from dental x-rays. However, no one should receive more radiation than necessary. A lead apron can be used to cover the body and reduce radiation exposure. Pregnant women should not have x-rays taken unless necessary.
Considerations
Dental x-rays can reveal dental cavities before they are clinically visible, even to the dentist. Many dentists will take yearly bitewings to look for early development of cavities in between the teeth.
Related Information
Impacted toothDental cavities
Periodontitis
Tooth abscess
Broken or dislocated jaw
Malocclusion of teeth
References
Dhar V. Diagnostic radiology in dental assessment. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 363.
Gold L, Williams TP. Odontogenic tumors: surgical pathology and management. In: Fonseca RJ, ed. Oral And Maxillofacial Surgery, Volume 2. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 18.
Nair MK, Levin MD, Nair UP. Radiographic interpretation. In: Berman LH, Hargreaves KM, Rotstein I, eds. Cohen's Pathways of the Pulp. 12th ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2021:chap 2.
Stefanac SJ, Benavides E, Callaghan C, et al. Digital tools for diagnosis and treatment planning. In: Stefanac SJ, Nesbit SP, eds. Diagnosis and Treatment Planning in Dentistry. 4th ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2024:chap 4.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 3/31/2024
Reviewed By: Michael Kapner, DDS, General Dentistry, Norwalk Medical Center, Norwalk CT. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2025 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
