Scrotal ultrasound
Testicular ultrasound; Testicular sonogram
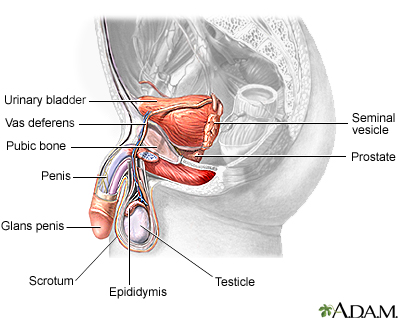
Scrotal ultrasound is an imaging test that looks at the scrotum. The scrotum is the flesh-covered sac that hangs between the legs at the base of the penis and contains the testicles.
The testicles are the male reproductive organs that produce sperm and the hormone testosterone. They are located in the scrotum, along with other small organs, blood vessels, and a small tube called the vas deferens.
Images
I Would Like to Learn About:
How the Test is Performed
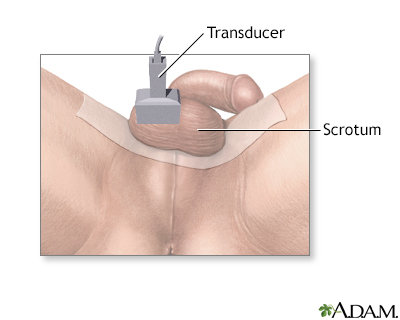
You will lie on your back with your legs spread. The health care provider drapes a cloth across your thighs under the scrotum or applies wide strips of adhesive tape to the area. The scrotal sac will be slightly raised with the testicles lying side by side.
A clear gel is applied to the scrotal sac to help transmit the sound waves. A handheld probe (the ultrasound transducer) is then moved over the scrotum by the technologist. The ultrasound machine sends out high-frequency sound waves. These waves reflect off areas in the scrotum to create a picture.
How to Prepare for the Test
No special preparation is needed for this test.
How the Test will Feel
There is little discomfort. The conducting gel may feel slightly cold and wet.
Why the Test is Performed
A testicle ultrasound is done to:
- Help determine why one or both testicles have become larger or smaller
- Look at a mass or lump in one or both of the testicles
- Find the reason for pain in the testicles
- Show how blood flows through the testicles
Normal Results
The testicles and other areas in the scrotum appear normal.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Possible causes of abnormal results include:
- Collection of very small veins, called a varicocele
- Infection or abscess
- Noncancerous (benign) cyst
- Twisting of the testicle that blocks blood flow, called testicular torsion
- Testicular tumor
- Testicular atrophy (shrinkage)
Risks
There are no known risks. You will not be exposed to radiation with this test.
Considerations
In certain cases, Doppler ultrasound may help identify blood flow inside the scrotum. This method can be helpful in cases of testicular torsion because blood flow to the twisted testicle may be reduced.
Related Information
TestesTestosterone
Scrotum
Penis
Ultrasound
X-ray
Cyst
Tumor
References
Gilbert BR, Fulgham PF. Urinary tract imaging: basic principles of urologic ultrasonography. In: Partin AW, Dmochowski RR, Kavoussi LR, Peters CA, eds. Campbell-Walsh-Wein Urology. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 4.
Owen CA. Scrotum. In: Hagen-Ansert SL, ed. Textbook of Diagnostic Sonography. 9th ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2023:chap 23.
Sommers D, Winter T. The scrotum. In: Rumack CM, Levine D, eds. Diagnostic Ultrasound. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 20.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 4/6/2024
Reviewed By: Jason Levy, MD, FSIR, Northside Radiology Associates, Atlanta, GA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2025 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
