Endocervical culture
Vaginal culture; Female genital tract culture; Culture - cervix
Endocervical culture is a laboratory test that helps identify infection in the female genital tract.
Images
I Would Like to Learn About:
How the Test is Performed
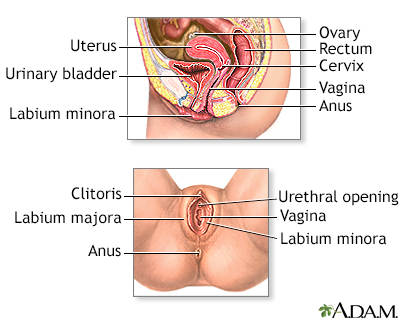
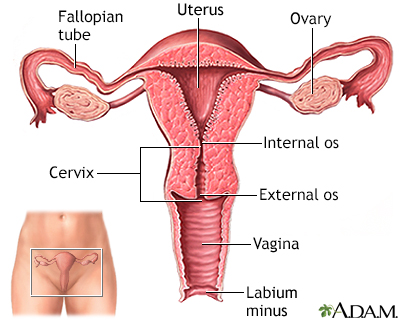
During a vaginal examination, the health care provider uses a swab to take samples of mucus and cells from the endocervix. This is the area around the opening of the uterus. The samples are sent to a lab. There, they are placed in a special dish (culture). They are then watched to see if bacteria, virus, or fungus grow. Further tests may be done to identify the specific organism and determine the best treatment.
How to Prepare for the Test
In the 2 days before the procedure:
- Do not use creams or other medicines in the vagina.
- Do not douche. (You should never douche. Douching can cause infection of the vagina or uterus.)
- Avoid intercourse.
- Empty your bladder and bowel.
- At your provider's office, follow instructions for preparing for the vaginal exam.
How the Test will Feel
You will feel some pressure from the speculum. This is an instrument inserted into the vagina to hold the area open so that the provider can view the cervix and collect the samples. There may be a slight cramping when the swab touches the cervix.
Why the Test is Performed
The test may be done to determine the cause of vaginitis, pelvic pain, an unusual vaginal discharge, or other signs of infection.
Normal Results
Organisms that are usually present in the vagina are there in the expected amounts.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Abnormal results indicate the presence of an infection in the genital tract or urinary tract in women, such as:
- Genital herpes
- Chronic swelling and irritation of the urethra (urethritis)
- Sexually transmitted infections, such as gonorrhea or chlamydia
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
Risks
There may be slight bleeding or spotting after the test. This is normal.
Related Information
Vaginal drynessVaginal itching and discharge - adult and adolescent
Chlamydia
Strep throat
Chlamydia infections in women
References
Eckert LO, Lentz GM. Genital tract infections: vulva, vagina, cervix, toxic shock syndrome, endometritis, and salpingitis. In: Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA, Lobo RA, eds. Comprehensive Gynecology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 23.
Swygard H, Cohen MS. Approach to the patient with a sexually transmitted infection. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 264.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 8/23/2023
Reviewed By: LaQuita Martinez, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Emory Johns Creek Hospital, Alpharetta, GA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2025 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
