DHEA-sulfate test
Serum DHEA-sulfate; Dehydroepiandrosterone-sulfate test; DHEA-sulfate - serum
DHEA stands for dehydroepiandrosterone. It is a hormone produced by the adrenal glands in both men and women. It can be converted to other hormones that have weak male (androgenic) effects. The DHEA-sulfate test measures the amount of DHEA-sulfate in the blood.
Images
I Would Like to Learn About:
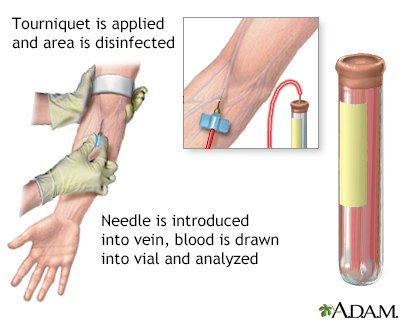
How the Test is Performed
A blood sample is needed.
How to Prepare for the Test
No special preparation is necessary. However, tell your health care provider if you are taking any vitamins or supplements that contain DHEA or DHEA-sulfate.
How the Test will Feel
When the needle is inserted to draw blood, some people feel moderate pain. Others feel only a prick or sting. Afterward, there may be some throbbing or a slight bruise. This soon goes away.
Why the Test is Performed
This test is done to check the function of the two adrenal glands. One of these glands sits above each kidney. They are one of the major sources of androgens in women.
Although DHEA-sulfate is the most abundant hormone in the body, its exact function is still not known.
- In men, the male hormone effect may not be important if testosterone level is normal.
- In women, DHEA contributes to normal libido and sexual satisfaction.
- DHEA may also have effects on the immune system.
The DHEA-sulfate test is often done in women who show signs of having excess male hormones. Some of these signs are male body changes, excess hair growth, oily skin, acne, irregular periods, or problems becoming pregnant.
It may also be done in women who are concerned about low libido or decreased sexual satisfaction who have pituitary or adrenal gland disorders.
The test is also done in children who are maturing too early (precocious puberty).
Normal Results
Normal blood levels of DHEA-sulfate can differ by sex and age.
Typical normal ranges for females are:
- Ages 18 to 29: 45 to 320 micrograms per deciliter (µg/dL) or 1.2 to 8.7 micromoles per liter (µmol/L)
- Ages 30 to 39: 40 to 325 µg/dL or 1.1 to 8.8 µmol/L
- Ages 40 to 49: 25 to 220 µg/dL or 0.7 to 6.0 µmol/L
- Ages 50 to 59: 15 to 170 µg/dL or 0.4 to 4.6 µmol/L
- Ages above 59: less than 145 µg/dL or less than 3.9 µmol/L
Typical normal ranges for males are:
- Ages 18 to 29: 110 to 510 micrograms per deciliter (µg/dL) or 3.0 to 14.0 micromoles per liter (µmol/L)
- Ages 30 to 39: 110 to 370 µg/dL or 3.0 to 10.0 µmol/L
- Ages 40 to 49: 45 to 345 µg/dL or 1.2 to 9.4 µmol/L
- Ages 50 to 59: 25 to 240 µg/dL or 0.7 to 6.5 µmol/L
- Ages above 59: less than 204 µg/dL or less than 5.5 µmol/L
Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Some labs use different measurements or test different specimens. Talk to your health care provider about the meaning of your specific test results.
What Abnormal Results Mean
An increase in DHEA-sulfate may be due to:
- A common genetic disorder called congenital adrenal hyperplasia.
- A tumor of the adrenal gland, which can be benign or be a cancer.
- A common problem in women younger than 50, called polycystic ovary syndrome.
- Body changes of a girl with puberty happening earlier than normal.
A decrease in DHEA sulfate may be due to:
- Adrenal gland disorders that produce lower than normal amounts of adrenal hormones, including adrenal insufficiency and Addison disease
- The pituitary gland not producing normal amounts of its hormones (hypopituitarism)
- Taking glucocorticoid medicines
DHEA levels normally decline with age in both men and women. There is no reliable evidence that taking DHEA supplements prevents aging-related conditions.
Risks
There is little risk involved with having your blood taken. Veins and arteries vary in size from one person to another and from one side of the body to the other. Obtaining a blood sample from some people may be more difficult than from others.
Other risks associated with having blood drawn are slight, but may include:
- Excessive bleeding
- Fainting or feeling lightheaded
- Multiple punctures to locate veins
- Hematoma (blood buildup under the skin)
- Infection (a slight risk any time the skin is broken)
Related Information
Adrenal glandsPrecocious puberty
References
Chen Zi-Chiang, Legro RS, Ehrmann DA, Wei D. Androgen excess disorders in women. In: Robertson RP, ed. DeGroot's Endocrinology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 124.
Haddad NG, Eugster EA. Endocrinology of pubertal disorders. In: Robertson RP, ed. DeGroot's Endocrinology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 103.
Nerenz RD, Boh B. Reproductive endocrinology and related disorders. In: Rifai N, Chiu RWK, Young I, Burnham CAD, Wittwer CA, eds. Tietz Textbook of Laboratory Medicine. 7th ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2023:chap 58.
Styne DM, Loomba LA. Endocrinology of sexual maturation and puberty. In: Robertson RP, ed. DeGroot's Endocrinology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 102.
van den Beld AW, Lamberts SWJ. Endocrinology and aging. In: Melmed S, Auchus RJ, Goldfine AB, Koenig RJ, Rosen CJ, eds. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 28.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 2/28/2024
Reviewed By: Sandeep K. Dhaliwal, MD, board-certified in Diabetes, Endocrinology, and Metabolism, Springfield, VA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2025 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
