Serum free hemoglobin test
Blood hemoglobin; Serum hemoglobin; Hemolytic anemia - free hemoglobin
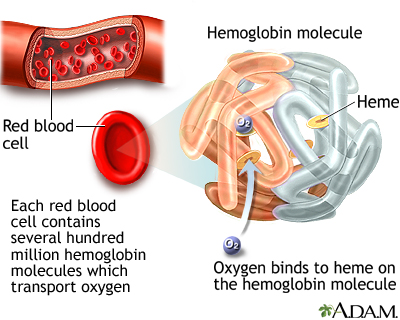
Serum free hemoglobin is a blood test that measures the level of free hemoglobin in the liquid part of the blood (the serum). Free hemoglobin is the hemoglobin outside of the red blood cells. Most of the hemoglobin is found inside the red blood cells, not in the serum. Hemoglobin carries oxygen in the blood.
Images
I Would Like to Learn About:
How the Test is Performed
A blood sample is needed.
How to Prepare for the Test
No preparation is necessary.
How the Test will Feel
When the needle is inserted to draw blood, some people feel moderate pain. Others feel only a prick or stinging. Afterward, there may be some throbbing or a slight bruise. This soon goes away.
Why the Test is Performed
Hemoglobin (Hb) is the main component of red blood cells. It is a protein that carries oxygen. This test is done to diagnose or monitor how severe hemolytic anemia is. This is a disorder in which a low red blood cell count is caused by the abnormal breakdown of red blood cells.
Normal Results
Plasma or serum in someone who does not have hemolytic anemia may contain up to 5 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or 0.05 grams per liter (g/L) hemoglobin.
Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Some labs use different measurements or may test different samples. Talk to your health care provider about the meaning of your specific test results.
What Abnormal Results Mean
A higher-than-normal level may indicate:
- Hemolytic anemia (due to any cause, including autoimmune and non-immune causes, such as thalassemia)
- Condition in which red blood cells break down when the body is exposed to certain medicines or the stress of infection (G6PD deficiency)
- Low red blood cell count due to red blood cells breaking down sooner than normal
- Blood disorder in which red blood cells are destroyed when they go from cold to warm temperatures (paroxysmal cold hemoglobinuria)
- Sickle cell disease
- Transfusion reaction
Risks
There is little risk involved with having your blood taken. Veins and arteries vary in size from one person to another and from one side of the body to the other. Obtaining a blood sample from some people may be more difficult than from others.
Other risks associated with having blood drawn are slight, but may include:
- Excessive bleeding
- Fainting or feeling lightheaded
- Multiple punctures to locate veins
- Hematoma (blood buildup under the skin)
- Infection (a slight risk any time the skin is broken)
Related Information
HemoglobinHemolytic anemia
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency
Hereditary spherocytic anemia
Paroxysmal cold hemoglobinuria (PCH)
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH)
Sickle cell disease
Thalassemia
Hemolytic transfusion reaction
References
Marcogliese AN, Hensch L. Resources for the hematologist: interpretive comments and selected reference values for neonatal, pediatric, and adult populations. In: Hoffman R, Benz EJ, Silberstein LE, et al, eds. Hematology: Basic Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 159.
Means RT. Approach to the anemias. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 144.
Review Date: 3/31/2024
Reviewed By: Todd Gersten, MD, Hematology/Oncology, Florida Cancer Specialists & Research Institute, Wellington, FL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2025 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
