Catecholamines - urine
Dopamine - urine test; Epinephrine - urine test; Adrenalin - urine test; Urine metanephrine; Normetanephrine; Norepinephrine - urine test; Urine catecholamines; VMA; HVA; Metanephrine; Homovanillic acid (HVA)
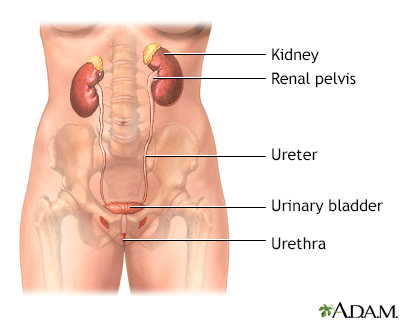
Catecholamines are chemicals made by nerve tissue (including the brain) and the adrenal gland.
The main types of catecholamines are dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine. These chemicals break down into other components, which leave your body through your urine.
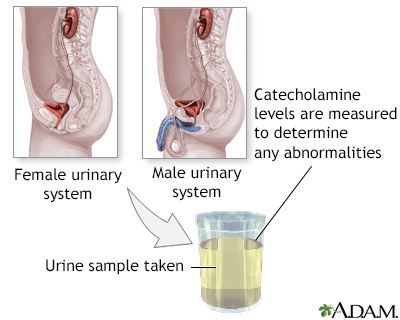
A urine test can be done to measure the amount of catecholamines produced by your body. Separate urine tests may be done to measure related substances.
Catecholamines can also be measured with a blood test.
Images
How the Test is Performed
For this test, you must collect your urine in a special bag or container every time you urinate for a 24-hour period.
- On day 1, urinate over the toilet when you wake up in the morning and discard that urine.
- Urinate into the special container every time you use the bathroom for the next 24 hours. Keep it in the refrigerator or a cool place during the collection period.
- On day 2, urinate into the container in the morning again when you wake up.
- Label the container with your name, the date, the time of completion, and return it as instructed.
For an infant, thoroughly wash the area where urine exits the body.
- Open a urine collection bag (a plastic bag with an adhesive paper on one end).
- For males, place the entire penis in the bag and attach the adhesive to the skin.
- For females, place the bag over the labia.
- Diaper as usual over the secured bag.
This procedure may take a few tries. An active baby can move the bag causing urine to go into the diaper.
Check the infant often and change the bag after the infant has urinated into it. Drain the urine from the bag into the container provided by your health care provider.
Deliver the sample to the laboratory or to your provider as soon as possible.
How to Prepare for the Test
Stress and heavy exercise may affect the test results.
Some foods can increase catecholamines in your urine. You may need to avoid the following foods and beverages for several days before the test:
- Bananas
- Chocolate
- Citrus fruits
- Cocoa
- Coffee
- Licorice
- Tea
- Vanilla
Many medicines can interfere with test results.
- Your provider will tell you if you need to stop taking any medicines before you have this test.
- Do not stop or change your medicines without talking to your provider first.
How the Test will Feel
The test involves only normal urination, and there is no discomfort.
Why the Test is Performed
The test is usually done to diagnose an adrenal gland tumor called pheochromocytoma. It may also be used to diagnose a nervous system tumor called neuroblastoma. Urine catecholamine levels are increased in most people with neuroblastoma.
The urine test for catecholamines may also be used to monitor those who are receiving treatment for these conditions.
Normal Results
All of the catecholamines are broken down into inactive substances that appear in the urine:
- Dopamine becomes homovanillic acid (HVA)
- Norepinephrine becomes normetanephrine and vanillylmandelic acid (VMA)
- Epinephrine becomes metanephrine and VMA
The following normal values are the amount of the substance found in the urine over a 24-hour period:
- Dopamine: 65 to 400 micrograms (mcg)/24 hours (420 to 2612 nmol/24 hours)
- Epinephrine: 0.5 to 20 mcg/24 hours
- Metanephrine: 24 to 96 mcg/24 hours (some laboratories give the range as 140 - 785 mcg/24 hours)
- Norepinephrine: 15 to 80 mcg/24 hours
- Normetanephrine: 75 to 375 mcg/24 hours
- Total urine catecholamines: 14 to 110 mcg/24 hours
- VMA: 2 to 7 milligrams (mg)/24 hours (10 to 35 mcmol/24 hours)
Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Talk to your provider about the meaning of your specific test results.
The examples above show the common measurements for results for these tests. Some laboratories use different measurements or may test different specimens.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Elevated levels of urinary catecholamines may indicate:
- Acute anxiety or severe stress
- Ganglioneuroblastoma (very rare)
- Ganglioneuroma (very rare)
- Neuroblastoma (rare)
- Pheochromocytoma (rare)
The test may also be performed for:
Risks
There are no risks.
Considerations
Several foods and drugs, as well as physical activity and stress, can affect the accuracy of this test.
Related Information
PheochromocytomaNeuroblastoma
Catecholamine blood test
Stress and your health
Ganglioneuroblastoma
Ganglioneuroma
Multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) II
References
Gruber HA, Oprea M. Russell YX. Evaluation of endocrine function. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 25.
Young WF. Adrenal medulla, catecholamines, and pheochromocytoma. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 209.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 8/20/2023
Reviewed By: Jacob Berman, MD, MPH, Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine, Division of General Internal Medicine, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2025 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
