Temperature measurement
The measurement of body temperature can help detect illness. It can also monitor whether or not treatment is working. A high temperature is a fever.
Images
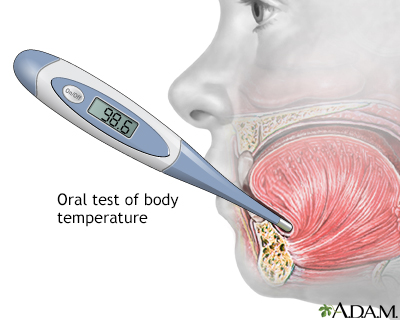
How the Test is Performed
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommends not to use glass thermometers with mercury. The glass can break, and mercury is a poison.
Electronic thermometers are most often suggested. An easy-to-read panel shows the temperature. The probe can be placed in the mouth, rectum, or armpit.
- Mouth: Place the probe under the tongue and close the mouth. Breathe through the nose. Use the lips to hold the thermometer tightly in place. Leave the thermometer in the mouth for 3 minutes or until the device beeps.
- Rectum: This method is for infants and small children. They cannot hold a thermometer safely in their mouth. Place petroleum jelly on the bulb of a rectal thermometer. Place the child face down on a flat surface or lap. Spread the buttocks and insert the bulb end about 1/2 to 1 inch (1 to 2.5 centimeters) into the anal canal. Be careful not to insert it too far. Struggling can push the thermometer in further. Remove after 3 minutes or when the device beeps.
- Armpit: Place the thermometer in the armpit. Press the arm against the body. Wait for 5 minutes before reading or when the device beeps.
Plastic strip thermometers change color to show the temperature. This method is the least accurate.
- Place the strip on the forehead. Read it after 1 minute while the strip is in place.
- Plastic strip thermometers for the mouth are also available.
Electronic ear thermometers are common. They are easy to use. However, some users report that the results are less accurate than with probe thermometers.
Electronic forehead thermometers are more accurate than ear thermometers and their accuracy is similar to probe thermometers.
How to Prepare for the Test
Always clean the thermometer before and after using. You can use cool, soapy water or rubbing alcohol.
Wait at least 1 hour after heavy exercise or a hot bath before measuring body temperature. Wait for 20 to 30 minutes after smoking, eating, or drinking a hot or cold liquid.
Normal Results
The average normal body temperature is 98.6°F (37°C). The normal temperature can vary due to things such as:
- Age (in children over 6 months, daily temperature can vary by 1 to 2 degrees Fahrenheit)
- Differences among individuals
- Time of day (often highest in the evening)
- Which type of measurement was taken (oral, rectal, forehead, or armpit)
You need to have an accurate temperature measurement to determine if a fever is present. Be sure to tell your health care provider which type of temperature measurement you used when discussing a fever.
The exact relationship between different types of temperature measurement is unclear. However, the following general guidelines for temperature results are used:
The average normal oral temperature is 98.6°F (37°C).
- A rectal temperature is 0.5°F (0.3°C) to 1°F (0.6°C) higher than an oral temperature.
- An ear temperature is 0.5°F (0.3°C) to 1°F (0.6°C) higher than an oral temperature.
- An armpit temperature is most often 0.5°F (0.3°C) to 1°F (0.6°C) lower than an oral temperature.
- A forehead scanner is most often 0.5°F (0.3°C) to 1°F (0.6°C) lower than an oral temperature.
Other factors to take into account are:
- In general, rectal temperatures are considered to be more accurate when checking for fever in a young child.
- Plastic strip thermometers measure skin temperature, not body temperature. They are not recommended for general home use.
What Abnormal Results Mean
If the reading on the thermometer is more than 1 to 1.5 degrees Fahrenheit above your normal temperature, you have a fever. Fevers may be a sign of:
- Blood clots
- Cancer
- Certain types of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus
- Diseases in the intestines, such as Crohn disease or ulcerative colitis
- Infection (both serious and non-serious)
- Many other medical problems
Body temperature can also be raised by:
- Being active
- Being in a high temperature or high humidity
- Eating
- Feeling strong emotions
- Menstruating
- Taking certain medicines
- Teething (in a young child -- but no higher than 100°F [37.7°C])
- Wearing heavy clothing
Body temperature that is too high or too low can be serious. Contact your provider if this is the case.
Related topics include:
Related Information
FeverReferences
McGrath JL, Bachmann DJ. Vital signs measurement. In: Roberts JR, Custalow CB, Thomsen TW, eds. Roberts and Hedges' Clinical Procedures in Emergency Medicine and Acute Care. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 1.
Sajadi MM, Romanovsky AA. Temperature regulation and the pathogenesis of fever. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 55.
Ward MA, Hannemann NL. Fever: pathogenesis and treatment. In: Cherry JD, Harrison GJ, Kaplan SL, Steinbach WJ, Hotez PJ, eds. Feigin and Cherry's Textbook of Pediatric Infectious Diseases. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 4.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 2/8/2024
Reviewed By: Linda J. Vorvick, MD, Clinical Professor, Department of Family Medicine, UW Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2024 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
