Electroretinography
ERG; Electrophysiologic testing
Electroretinography is a test to measure the electrical response of the eye's light-sensitive cells, called rods and cones. These cells are part of the retina (the back part of the eye).
Images
How the Test is Performed
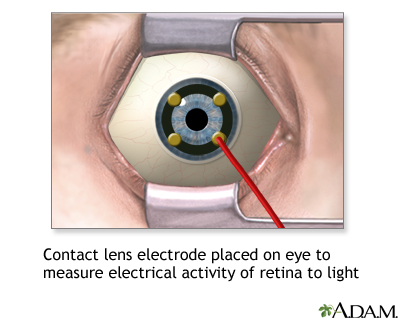
While you are in a sitting position, the health care provider places numbing drops into your eyes, so you will not have any discomfort during the test. Your eyes are held open with a small device called a speculum. An electrical sensor (electrode) is placed on each eye.
The electrode measures the electrical activity of the retina in response to light. A light flashes, and the electrical response travels from the electrode to a TV-like screen, where it can be viewed and recorded. The normal response pattern has waves called A and B.
The provider will take the readings in normal room light and then again in the dark, after allowing 20 minutes for your eyes to adjust.
How to Prepare for the Test
No special preparation is necessary for this test.
How the Test will Feel
The probes that rest on your eye may feel a little scratchy. The test takes about 1 hour to perform.
Why the Test is Performed
This test is done to detect disorders of the retina. It is also useful for determining if retinal surgery is recommended.
Normal Results
Normal test results will show a normal A and B pattern in response to each flash.
What Abnormal Results Mean
The following conditions may cause abnormal results:
- Arteriosclerosis with damage to the retina
- Congenital night blindness
- Congenital retinoschisis (splitting of the retinal layers)
- Giant cell arteritis
- Medicines (chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine)
- Mucopolysaccharidosis
- Retinal detachment
- Rod-cone dystrophy (retinitis pigmentosa)
- Trauma
- Vitamin A deficiency
Risks
The cornea may get a temporary scratch on the surface from the electrode. Otherwise, there are no risks with this procedure.
Considerations
You should not rub your eyes for an hour after the test, as this could injure the cornea. Your provider will talk to you about the results of the test and what they mean for you.
Related Information
Retinitis pigmentosaAtherosclerosis
Giant cell arteritis
Mucopolysaccharides
Retinal detachment
Vitamin A
References
Baloh RW, Jen JC. Neuro-ophthalmology. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 392.
Reichel E, Klein K, Richard A. Retinal electrophysiology. In: Yanoff M, Duker JS, eds. Ophthalmology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 6.7.
Tsang SH, Holder GE. Clinical electrophysiology. In: Sadda SVR, Sarraf D, Freund B, et al, eds. Ryan's Retina. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 9.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 8/5/2024
Reviewed By: Franklin W. Lusby, MD, Ophthalmologist, Lusby Vision Institute, La Jolla, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2025 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
