Sutures - ridged
Ridged sutures
Ridged sutures refer to an overlap of the bony plates of the skull in an infant, with or without early closure.
Images
I Would Like to Learn About:
Considerations
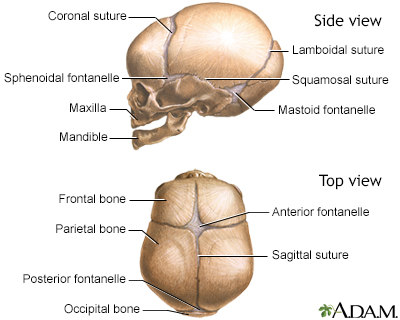
The skull of an infant or young child is made up of bony plates that allow for growth of the skull. The borders where these plates intersect are called sutures or suture lines. In an infant only a few minutes old, the pressure from delivery compresses the head. This makes the bony plates overlap at the sutures and creates a small ridge.
This is normal in newborns. In the next few days, the head expands and the overlapping disappears. The edges of the bony plates meet edge-to-edge. This is the normal position.
Ridging of the suture line can also occur when the bony plates fuse together too early. When this happens, growth along that suture line stops. Premature closure generally leads to an unusually shaped skull.
Premature closing of the suture running the length of the skull (sagittal suture) produces a long, narrow head. Premature closing of the suture that runs from side-to-side on the skull (coronal suture) leads to a short, wide head.
Causes
Causes may include:
- Normal ridging due to overlap of bony plates after birth
- Congenital craniosynostosis
- Crouzon syndrome
- Apert syndrome
- Carpenter syndrome
- Pfeiffer syndrome
Home Care
Home care depends on the condition causing the premature closure of sutures.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider if:
- You notice a ridge along the suture line of your child's head.
- You think that your child has an abnormal head shape.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your provider will get a medical history and will do a physical exam.
Medical history questions might include:
- When did you first notice that the skull seemed to have ridges in it?
- What do the soft spots (fontanelles) look like?
- Have the fontanelles closed? At what age did they close?
- What other symptoms are present?
- How has your child been developing?
Your provider will examine the skull to see if there is ridging. If there is ridging, your child might need x-rays or other types of scans of the skull to show whether the sutures have closed too early.
Although your provider keeps records from routine checkups, you may find it helpful to keep your own records of your child's development. Bring these records to your provider's attention if you notice anything unusual.
References
Ball JW, Dains JE, Flynn JA, Solomon BS, Stewart RW. Head and neck. In: Ball JW, Dains JE, Flynn JA, Solomon BS, Stewart RW, eds. Seidel's Guide to Physical Examination. 10th ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2023:chap 11.
Goyal NK. The newborn infant. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 113.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 1/24/2023
Reviewed By: Neil K. Kaneshiro, MD, MHA, Clinical Professor of Pediatrics, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2024 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
