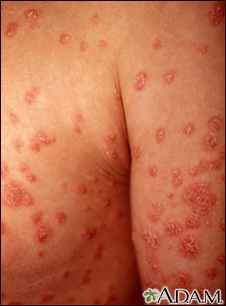
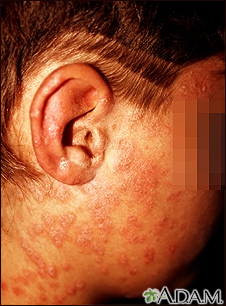
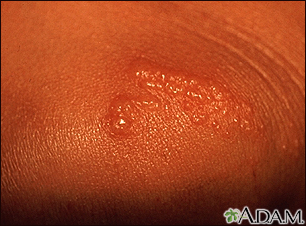
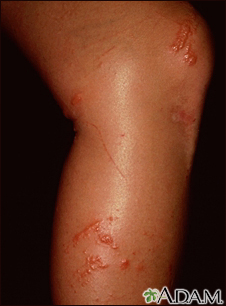
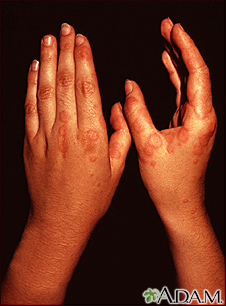
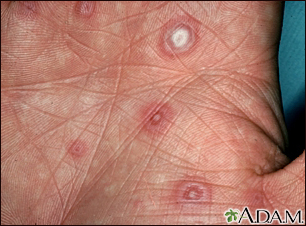
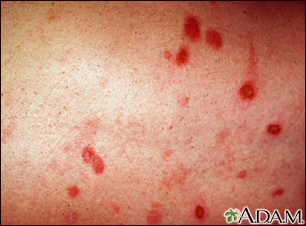
Rashes
Skin redness or inflammation; Skin lesion; Rubor; Skin rash; Erythema
Rashes involve changes in the color, feeling or texture of your skin.
Images

I Would Like to Learn About:
Considerations
Often, the cause of a rash can be determined from how it looks and its location and symptoms. Skin testing, such as a scraping, culture, or biopsy, may also be used to help with diagnosis. Sometimes, the cause of the rash remains unknown.
Causes
A rash is often due to dermatitis, meaning inflammation of the skin. Contact dermatitis is caused by things your skin touches, such as:
- Chemicals in elastic, latex, and rubber products
- Cosmetics, soaps, and detergents
- Dyes and other chemicals in clothing
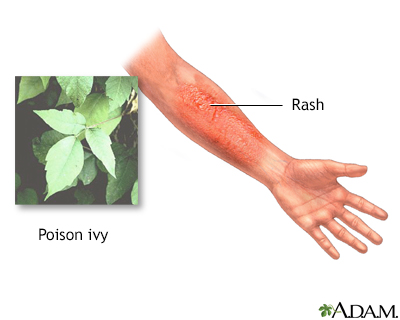
- Poison ivy, oak, or sumac
Seborrheic dermatitis is a rash that appears in patches of redness and scaling around the eyebrows, eyelids, mouth, nose, trunk, and behind the ears. If it happens on your scalp, it is called dandruff in adults and cradle cap in infants.
Age, stress, fatigue, weather extremes, oily skin, infrequent shampooing, and alcohol-based lotions aggravate this harmless but bothersome condition.
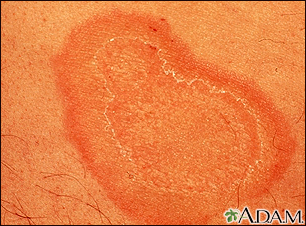
Other common causes of a rash include:
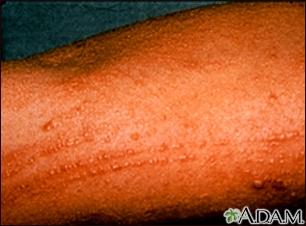
- Eczema (atopic dermatitis) -- Tends to happen in people with allergies or asthma. The rash is generally red, itchy, and scaly.
- Psoriasis -- Tends to occur as red, scaly, patches over joints and along the scalp. It is sometimes itchy. Fingernails may also be affected.
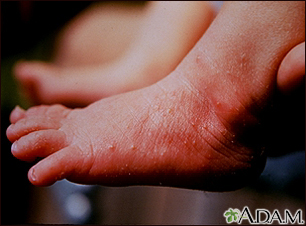
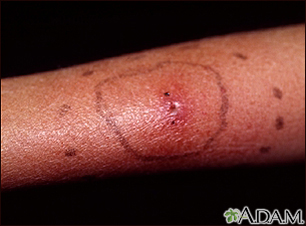
- Impetigo -- Common in children, this infection is from bacteria that live in the top layers of the skin. It appears as red sores that turn into blisters, ooze, then form a honey colored crust over all or part of the rash.
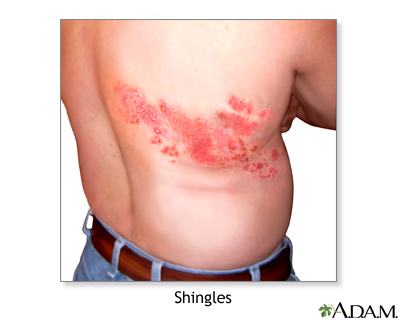
- Shingles -- A painful blistered skin condition caused by the same virus as chickenpox. The virus can lie dormant in your body for many years and re-emerge as shingles. It usually affects only one side of the body.
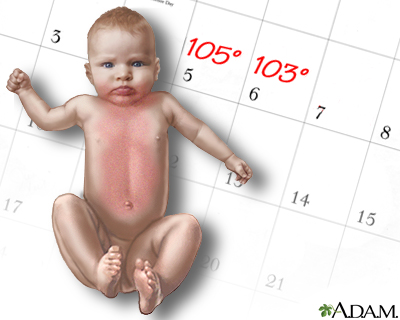
- Childhood illnesses such as chickenpox, measles, roseola, rubella, hand-foot-mouth disease, fifth disease, and scarlet fever.
- Medicines
- Insect bites or stings.
Many medical conditions can cause a rash as well. These include:
- Lupus erythematosus (an immune system disease)
- Rheumatoid arthritis, especially the juvenile type
- Kawasaki disease (inflammation of the blood vessels)
- Certain body-wide (systemic) viral, bacterial or fungal infections
Home Care
Many simple rashes will improve with gentle skin care and by avoiding irritating substances. Follow these general guidelines:
- Avoid scrubbing your skin.
- Use gentle cleansers.
- Avoid applying cosmetic lotions or ointments directly on the rash.
- Use warm (not hot) water for cleaning. Pat dry, don't rub.
- Stop using any recently added cosmetics or lotions.
- Leave the affected area exposed to the air as much as possible.
- Try calamine medicated lotion for poison ivy, oak, or sumac, as well as for other types of contact dermatitis.
Hydrocortisone cream (1%) is available without a prescription and may soothe many rashes. Stronger hydrocortisone or other steroid creams are available with a prescription. If you have eczema, apply moisturizers over your skin. Try oatmeal bath products, available at drugstores, to relieve symptoms of eczema or psoriasis. Oral antihistamines may help relieve itchy skin.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call 911 or the local emergency number if:
- You are short of breath, your throat is tight, or your face is swollen.
- Your child has a purple rash that looks like a bruise.
Contact your health care provider if:
- You have joint pain, fever, or a sore throat.
- You have streaks of redness, swelling, or very tender areas as these may indicate an infection.
- You are taking a new medicine. Do not change or stop any of your medicines without contacting your provider.
- You may have a tick bite.
- Home treatment doesn't work, or your symptoms get worse.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your provider will perform a physical exam and ask about your medical history and symptoms. Questions may include:
- When did the rash begin?
- What parts of your body are affected?
- Does anything make the rash better? Worse?
- Have you used any new soaps, detergents, lotions, or cosmetics recently?
- Have you been in any wooded areas recently?
- Have you noticed a tick or insect bite?
- Have you had any change in your medicines?
- Have you eaten anything unusual?
- Do you have any other symptoms, like itching or scaling?
- What medical problems do you have, such as asthma or allergies?
- Have you recently traveled out of the area where you live?
Tests may include:
- Allergy testing
- Blood tests
- Skin biopsy
- Skin scrapings
Depending on the cause of your rash, treatments may include medicated creams or lotions, medicines taken by mouth, or skin surgery.
Many primary care providers are comfortable dealing with common rashes. For more complicated skin disorders, you may need a referral to a dermatologist.
Related Information
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)References
James WD, Elston DM, Treat JR, Rosenbach MA, Neuhaus IM. Cutaneous signs and diagnosis. In: James WD, Elston DM, Treat JR, Rosenbach MA, Neuhaus IM, eds. Andrews' Diseases of the Skin. 13th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 2.
Ko CJ. Approach to skin diseases. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 403.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 10/14/2024
Reviewed By: Elika Hoss, MD, Assistant Professor of Dermatology, Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, AZ. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2025 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
