Eyes - bulging
Protruding eyes; Exophthalmos; Proptosis; Bulging eyes
Bulging eyes is the abnormal protrusion (bulging out) of one or both eyeballs.
Images
Considerations
Prominent eyes may be a family trait. But prominent eyes are not the same as bulging eyes. Bulging eyes should be checked by a health care provider.
Bulging of one eye, especially in a child, can be a very serious sign. It should be checked right away.
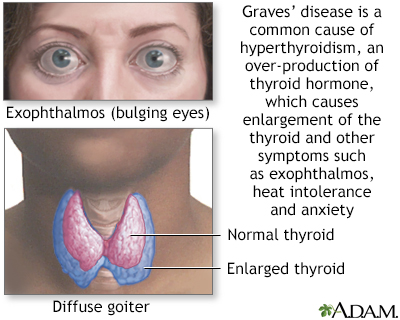
Hyperthyroidism (particularly Graves disease) is the most common medical cause of bulging eyes. With this condition, the eyes do not blink often and seem to have a staring quality.
Normally, there should be no visible white between the top of the iris (the colored part of the eye) and the upper eyelid. Seeing white in this area most often is a sign that the eye is bulging.
Because eye changes most often develop slowly, family members may not notice it until the condition is fairly advanced. Photos often draw attention to the bulging when it may have gone unnoticed before.
Causes
Causes may include:
- Glaucoma
- Graves disease
- Hemangioma
- Histiocytosis
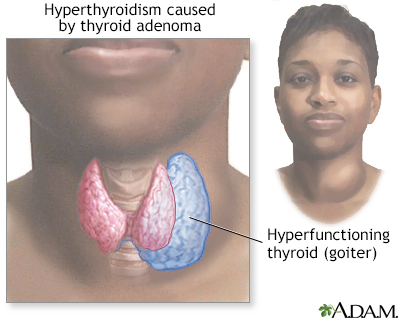
- Hyperthyroidism
- Leukemia
- Neuroblastoma
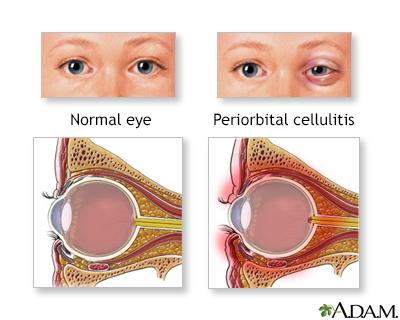
- Orbital cellulitis or periorbital cellulitis
- Rhabdomyosarcoma
Home Care
The cause needs to be diagnosed and treated by a provider. Because bulging eyes can cause a person to be self-conscious, emotional support is important.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if:
- You have bulging eyes and the cause has not yet been diagnosed.
- Bulging eyes are accompanied by other symptoms, such as pain or fever.
The provider will ask about your medical history and do a physical exam.
Some questions you may be asked include:
- Are both eyes bulging?
- When did you first notice bulging eyes?
- Is it getting worse?
- Do you have pain in your eyes?
- What other symptoms do you have?
A slit-lamp examination may be done. Blood testing for thyroid disease may be done.
Treatments depend on the cause. Artificial tears may be given to lubricate the eye to protect its surface (cornea).
Related Information
HyperthyroidismGraves disease
References
Cioffi GA, Liebmann JM. Diseases of the visual system. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 391.
Olitsky SE, Marsh JD. Orbital abnormalities. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 673.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 1/1/2025
Reviewed By: Linda J. Vorvick, MD, Clinical Professor Emeritus, Department of Family Medicine, UW Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2025 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
