Parathyroid gland removal
Removal of parathyroid gland; Parathyroidectomy; Hyperparathyroidism - parathyroidectomy; PTH - parathyroidectomy
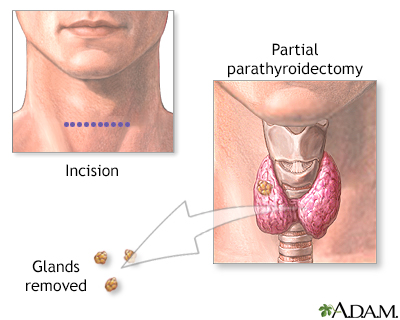
Parathyroidectomy is surgery to remove the parathyroid glands or parathyroid tumors. The parathyroid glands are right behind your thyroid gland in your neck. These glands help your body control the calcium level in the blood.
Images
Presentation
Description
You will receive general anesthesia (asleep and pain-free) for this surgery.
Usually the parathyroid glands are removed using a 2- to 4-inch (5- to 10-cm) surgical cut on your neck. During surgery:
- The cut is usually made in the center of your neck just under your Adam's apple.
- Your surgeon will look for the four parathyroid glands and remove any that are diseased.
- You may have a special blood test during surgery that will tell if all the diseased glands were removed.
- In rare cases, when all four of these glands need to be removed, part of one is transplanted into the forearm. Or, it is transplanted into a muscle in the front of your neck next to the thyroid gland. This helps ensure your body's calcium level stays at a healthy level.
The specific type of surgery depends on where the diseased parathyroid glands are. Types of surgery include:
- Minimally invasive parathyroidectomy. You may receive a shot of a very small amount of radioactive tracer before this surgery. This helps highlight the diseased glands. If you have this shot, your surgeon will use a special probe, like a Geiger counter, to locate the parathyroid gland. Your surgeon will make a small cut (1 to 2 inches; or 2.5 to 5 cm) on one side of your neck, and then remove the diseased gland through it. This procedure takes about 1 hour.
- Video-assisted parathyroidectomy. Your surgeon will make two small cuts in your neck. One is for instruments, and the other is for a camera. Your surgeon will use the camera to view the area and will remove the diseased glands with the instruments.
- Endoscopic parathyroidectomy. Your surgeon will make two or three small cuts in the front of your neck and one cut above the top of your collarbone. This reduces visible scarring, pain, and recovery time. This cut is less than 2 inches (5 cm) long. The procedure to remove any diseased parathyroid glands is similar to video-assisted parathyroidectomy.
Why the Procedure Is Performed
Your health care provider may recommend this surgery if one or more of your parathyroid glands is producing too much parathyroid hormone. This condition is called hyperparathyroidism. It is often caused by a small non-cancerous (benign) tumor called an adenoma.
Your surgeon will consider many factors when deciding whether to do surgery and what type of surgery would be best for you. Some of these factors are:
- Your age
- Calcium levels in your urine and blood
- Whether you have symptoms
Risks
Risks of anesthesia and surgery in general are:
- Reactions to medicines or breathing problems
- Bleeding, blood clots, or infection
Risks of parathyroidectomy are:
- Injury to the thyroid gland or the need to remove part of the thyroid gland.
- Hypoparathyroidism (parathyroid glands not producing enough parathyroid hormone). This can lead to low calcium levels that are dangerous to your health.
- Injury to the nerves going to the muscles that move your vocal cords. You may have a hoarse or weaker voice which could be temporary or permanent.
- Difficulty breathing. This is very rare and almost always goes away several weeks or months after surgery.
Before the Procedure
Parathyroid glands are very small. You may need to have tests that show exactly where your glands are. This will help your surgeon find your parathyroid glands during surgery. Two of the tests you may have are a CT scan and an ultrasound.
Tell your surgeon:
- If you are or might be pregnant
- What medicines, vitamins, herbs, and other supplements you're taking, even ones you bought without a prescription
During the week before your surgery:
- Fill any prescriptions for pain medicine and calcium you'll need after surgery.
- You may be asked to stop taking blood thinners. These include NSAIDs (aspirin, ibuprofen), vitamin E, warfarin (Coumadin), dabigatran (Pradaxa), rivaroxaban (Xarelto), apixaban (Eliquis), and clopidegrel (Plavix).
- Ask your surgeon which drugs you should still take on the day of your surgery.
On the day of your surgery:
- Follow instructions about not eating and drinking.
- Take the medicines your surgeon told you to take with a small sip of water.
- Arrive at the hospital on time.
After the Procedure
Often, people can go home the same day they have surgery. You can start your everyday activities in a few days. It will take about 1 to 3 weeks for you to fully heal.
The surgery area must be kept clean and dry. You may need to drink liquids and eat soft foods for a day.
Contact your surgeon if you have any numbness or tingling around your mouth in the 24 to 48 hours after surgery. This is caused by low calcium. Follow instructions about how to take your calcium supplements.
After this procedure, you should have routine blood tests to check your calcium level.
Outlook (Prognosis)
People usually recover soon after this surgery. Recovery may be faster when less invasive techniques are used.
Sometimes, another surgery is needed to remove more of the parathyroid glands.
Related Information
HypoparathyroidismParathyroid hormone (PTH) blood test
Hyperparathyroidism
Parathyroid cancer
Surgical wound care - open
References
Bobanga I, McHenry CR. The parathyroid glands. In: Townsend CM Jr, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM, Mattox KL, eds. Sabiston Textbook of Surgery. 21st ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2022:chap 38.
Coan KE, Wang TS. Primary Hyperparathyroidism. In: Cameron JL, Cameron AM, eds. Current Surgical Therapy. 13th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:779-785.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 8/22/2022
Reviewed By: Debra G. Wechter, MD, FACS, General Surgery Practice Specializing in Breast Cancer, Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2024 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
