Boils
Furuncle
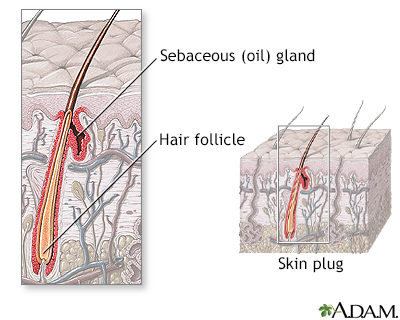
A boil is an infection that affects groups of hair follicles and nearby skin tissue.
Related conditions include folliculitis, an inflammation of one or more hair follicles, and carbunculosis, a skin infection that often involves a group of hair follicles.
Images
Causes
Boils are very common. They are most often caused by the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus. They can also be caused by other types of bacteria or fungi found on the skin's surface. Damage to the hair follicle allows the infection to grow deeper into the follicle and the tissues under it.
Boils may occur in the hair follicles anywhere on the body. They are most common on the face, neck, armpit, buttocks, and thighs. You may have one or many boils. The condition may occur only once or it can be a long-lasting (chronic) or a recurring problem.
Symptoms
A boil may begin as tender, pinkish-red, and swollen spot, on a firm area of the skin. Over time, it will feel like a water-filled balloon or cyst.
The pain gets worse as it fills with pus and dead tissue. It lessens when the boil drains. A boil may drain on its own. More often, the boil needs to be opened to drain.
The main symptoms of a boil include:
- A bump about the size of a pea, but may be as large as a golf ball
- White or yellow center (pustules)
- Spread to other skin areas or joining with other boils
- Quick growth
- Weeping, oozing, or crusting
Other symptoms may include:
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider can usually diagnose a boil based on how it looks. A sample of fluid from the boil may be sent to the lab for a culture to look for staphylococcus or other bacteria.
Treatment
Boils may heal on their own after a period of itching and mild pain. More often, they become more painful as pus builds up.
Boils usually need to open and drain in order to heal. This most often happens within 2 weeks. You should:
- Put warm, moist, compresses on the boil several times a day to speed draining and healing.
- Never squeeze a boil or try to cut it open at home. This can spread the infection.
- Continue to put warm, wet, compresses on the area after the boil opens.
You may need to have surgery to drain deep or large boils. Get treatment from your provider if:
- You have a fever or other symptoms with the boil.
- The boil causes pain or discomfort.
- You have a boil on your spine or the middle of your face.
- A boil lasts longer than 1 week.
- A boil that comes back.
It is important to keep a boil clean. To do this:
- Clean boils and change their dressing often.
- Wash your hands well before and after touching a boil.
- Do not reuse or share washcloths or towels. Wash clothing, washcloths, towels, and sheets or other items that have touched infected areas in hot water.
- Throw out used dressings in a sealed bag so that fluid from the boil does not touch anything else.
Your provider may give you antibiotics to take by mouth or a shot, if the boil is very bad or comes back.
Antibacterial soaps and creams cannot help much once a boil has formed.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Some people have repeated boils.
Boils in areas such as the ear canal or nose can be very painful.
Boils that form close together may expand and join, causing a condition called carbunculosis.
Possible Complications
These complications may occur:
- Abscess of the skin, spinal cord, brain, kidneys, or other organ
- Brain infection
- Heart infection
- Bone infection
- Infection of the blood or tissues (sepsis)
- Spinal cord infection
- Spread of infection to other parts of the body or skin surfaces
- Permanent scarring
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if boils:
- Appear on your face or spine
- Occur along with a fever, red streaks coming out from the sore, a large build-up of fluid in the area, or other symptoms of infection
- Cause pain or discomfort
- Do not heal with home treatment within 1 week
- Come back after treatment
Prevention
The following may help prevent the spread of infection:
- Antibacterial soaps
- Antiseptic (germ-killing) washes
- Keeping clean (such as thorough hand washing)
Related Information
CarbuncleSubcutaneous
Skin nodules
Abscess
Sepsis
Osteomyelitis
Endocarditis
Brain abscess
Spinal cord abscess
References
Dinulos JGH. Bacterial infections. In: Dinulos JGH, ed. Habif's Clinical Dermatology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 9.
Pulia M, May LS. Skin and soft tissue infections. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 126.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 10/14/2024
Reviewed By: Elika Hoss, MD, Assistant Professor of Dermatology, Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, AZ. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2025 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
