Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
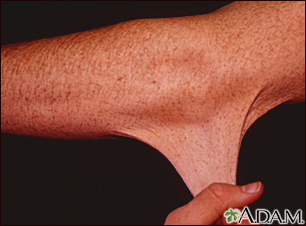
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) is a group of inherited disorders marked by extremely loose joints, very stretchy (hyperelastic) skin that bruises easily, and easily damaged blood vessels.
Images
I Would Like to Learn About:
Causes
There are at least 13 types of EDS. Hypermobile EDS is the most common type (90% of cases). Other forms include the classic and vascular forms.
A variety of gene variations cause problems with collagen. This is the material that provides strength and structure to:
- Skin
- Bone
- Blood vessels
- Internal organs
The variant collagen leads to the symptoms associated with EDS. In some forms of the syndrome, the rupture of internal organs or abnormal heart valves can occur.
Family history is a risk factor in some cases.
Symptoms
Symptoms of EDS vary by type and may include:
- Back pain
- Double-jointedness
- Easily damaged, bruised, and stretchy skin
- Easy scarring and poor wound healing
- Flat feet
- Increased joint mobility, joints popping, early arthritis
- Joint dislocation
- Joint pain
- Premature rupture of membranes during pregnancy
- Very soft and velvety skin
- Vision problems
Exams and Tests
An exam by your health care provider may show:
- Deformed surface of the eye (cornea)
- Excess joint looseness and joint hypermobility
- Mitral valve in the heart does not close tightly (mitral valve prolapse)
- Gum infection (periodontitis)
- Rupture of intestines, uterus, or eyeball (seen only in vascular EDS, which is rare)
- Soft, thin, or very stretchy skin
Tests to diagnose EDS include:
- Collagen typing (performed on a skin biopsy sample)
- Collagen gene variation testing for some types of EDS
- Echocardiogram (heart ultrasound)
- Lysyl hydroxylase or oxidase activity (to check collagen formation)
Treatment
There is no specific cure for EDS. Individual problems and symptoms are evaluated and cared for appropriately. Physical therapy or an evaluation by a specialist in rehabilitation medicine is often needed.
Support Groups
More information and support for people with Ehlers-Danlos and their families can be found at:
The Ehlers-Danlos Society -- www.ehlers-danlos.com/support/
Outlook (Prognosis)
People with EDS generally have a normal life span. Intelligence is normal.
Those with the rare vascular type of EDS are at greater risk for rupture of a major organ or blood vessel. These people have a high risk for sudden death.
Possible Complications
Possible complications of EDS include:
- Chronic joint pain
- Early-onset arthritis
- Failure of surgical wounds to close (or stitches tear out)
- Premature rupture of membranes during pregnancy
- Rupture of major vessels, including a ruptured aortic aneurysm (only in vascular EDS)
- Rupture of a hollow organ such as the uterus or bowel (only in vascular EDS)
- Rupture of the eyeball (only in vascular EDS)
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider for an appointment if you have a family history of EDS and you are concerned about your risk or are planning to start a family.
Contact your provider for an appointment if you or your child has symptoms of EDS.
Prevention
Genetic counseling is recommended for prospective parents with a family history of EDS. Those planning to start a family should be aware of the type of EDS they have and how it is passed down to children. This can be determined through testing and evaluations suggested by your provider or genetic counselor.
Identifying any significant health risks may help prevent severe complications by vigilant screening and lifestyle alterations.
Related Information
Hyperelastic skinAbdominal aortic aneurysm
References
Basel D. Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 744.
Bober NP-H, Michael B, Krakow D. Heritable diseases of connective tissue. In: Firestein GS, McInnes IB, Koretzky GA, Mikuls TR, Neogi T, O'Dell JR, eds. Firestein & Kelly's Textbook of Rheumatology. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 107.
Pyeritz RE. Inherited diseases of connective tissue. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 239.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 11/6/2024
Reviewed By: Anna C. Edens Hurst, MD, MS, Associate Professor in Medical Genetics, The University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2025 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
