Creeping eruption
Parasite infection - hookworm; Cutaneous larvae migrans; Zoonotic hookworm; Ancylostoma caninum; Ancylostoma braziliensis; Bunostomum phlebotomum; Uncinaria stenocephala
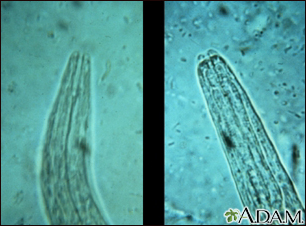
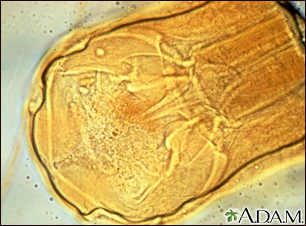
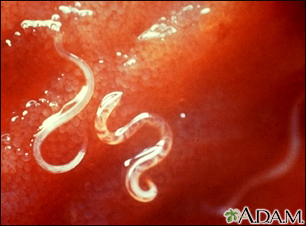
Creeping eruption is a human infection with dog or cat hookworm larvae (immature worms).
Images
Causes
Hookworm eggs are found in the stool of infected dogs and cats. When the eggs hatch, the larvae can infest soil and vegetation.
When you come into contact with this infested soil, the larvae can burrow into your skin. They cause an intense inflammatory response that leads to a rash and severe itching.
Creeping eruption is more common in countries with warm climates. In the United States, the Southeast has the highest rates of infection. The main risk factor for this disease is contact with damp, sandy soil that has been contaminated with infected cat or dog stool. More children than adults become infected.
Symptoms
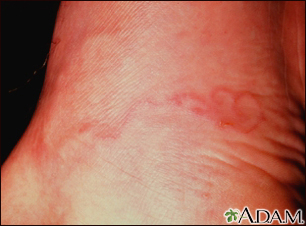
Symptoms of creeping eruption include:
- Blisters
- Itching, may be more severe at night
- Raised, snakelike tracks in the skin that may spread over time, usually about 1 centimeter (cm) or less than one-half inch (in) per day, usually on the feet and legs (severe infections may cause several tracks)
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider can often diagnose this condition by looking at your skin. In rare cases, a skin biopsy is done to check for other conditions. In very rare cases, a blood test is done to see if you have increased eosinophils (a type of white blood cell).
Treatment
Anti-parasitic medicines may be used to treat the infection.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Creeping eruption often goes away by itself over weeks to months. Treatment with anti-parasitic medicines helps the infection go away more quickly.
Possible Complications
Creeping eruption may lead to these complications:
- Bacterial skin infections caused by scratching
- Spread of the infection through the bloodstream to the lungs or small intestine (rare)
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you or your child have skin sores that are:
- Snake-like
- Itchy
- Moving from one area to another
Prevention
Public sanitation and deworming of dogs and cats have decreased hookworm infestation in the United States.
Hookworm larvae often enter the body through bare feet, so wearing shoes in areas where hookworm infestations are known to occur helps prevent infection.
Related Information
RashesHookworm infection
Immune response
References
Dinulos JGH. Infestations and bites. In: Dinulos JGH, ed. Habif's Clinical Dermatology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 15.
Dobbs KR, Dent AE. Toxocariasis (visceral and ocular larva migrans). In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 344.
Nash TE. Visceral larva migrans and other uncommon helminth infections. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 290.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 11/10/2024
Reviewed By: Jatin M. Vyas, MD, PhD, Professor in Medicine, Harvard Medical School; Associate in Medicine, Division of Infectious Disease, Department of Medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2025 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
