Mesenteric artery ischemia
Mesenteric vascular disease; Ischemic colitis; Ischemic bowel - mesenteric; Dead bowel - mesenteric; Dead gut - mesenteric; Atherosclerosis - mesenteric artery; Hardening of the arteries - mesenteric artery; Ischemic necrosis - mesenteric artery
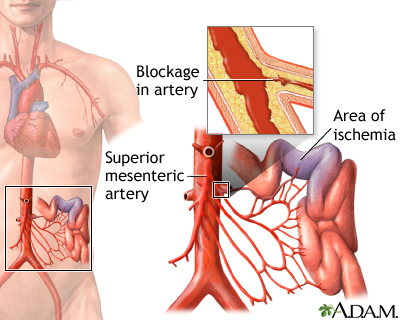
Mesenteric artery ischemia occurs when there is a narrowing or blockage of one or more of the three major arteries that supply the small and large intestines. These are called the mesenteric arteries.
Images
I Would Like to Learn About:
Causes
The arteries that supply blood to the intestines run directly from the aorta. The aorta is the main artery from the heart.
Hardening of the arteries occurs when fat, cholesterol, and other substances build up in the walls of arteries. This is more common in smokers and in people with high blood pressure or high blood cholesterol.
This narrows the blood vessels and reduces blood flow to the intestines. Like every other part of the body, blood brings oxygen to the intestines. When the oxygen supply is reduced, symptoms may occur.
The blood supply to the intestines may be suddenly blocked by a blood clot (embolus). The clots most often come from the heart or aorta. These clots are more commonly seen in people with abnormal heart rhythm.
Symptoms
Symptoms caused by gradual hardening of the mesenteric arteries include:
- Abdominal pain after eating
- Diarrhea
Symptoms of sudden (acute) mesenteric artery ischemia due to a traveling blood clot include:
- Sudden severe abdominal pain or bloating
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
- Fever
- Nausea
Exams and Tests
When symptoms begin suddenly or become severe, blood tests may show increased white blood cell count and changes in the blood acid level. There may be blood in the stool. Typically pain starts first and is followed by rectal bleeding.
A Doppler ultrasound or CT angiogram scan may show problems with the blood vessels and the intestine.
A mesenteric angiogram is a test that involves injecting a special dye into your bloodstream to highlight the arteries of the intestine. Then x-rays are taken of the area. This can show the location of the blockage in the artery.
Treatment
When the blood supply is blocked to a part of the heart muscle, the muscle will die. This is called a heart attack. A similar type of injury can occur to any part of the intestines.
When the blood supply is suddenly cut off by a blood clot, it is an emergency. Treatment can include medicines to dissolve the blood clots and open up the arteries.
If you have symptoms due to hardening of the mesenteric arteries, there are things you can do to control the problem:
- Stop smoking. Smoking narrows the arteries. This decreases the ability of the blood to carry oxygen and increases the risk of forming clots (thrombi and emboli).
- Make sure your blood pressure is under control.
- If you are overweight, reduce your weight.
- If your cholesterol is high, eat a low-cholesterol and low-fat diet.
- Monitor your blood sugar level if you have diabetes, and keep it under control.
Surgery may be done if the problem is severe.
- The blockage is removed and the arteries are reconnected to the aorta. A bypass around the blockage is another procedure. It is usually done with a plastic tube graft.
- Insertion of a stent. A stent may be used as an alternative to surgery to enlarge the blockage in the artery or to deliver medicine directly to the affected area.
- At times, a portion of your intestine will need to be removed.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The outlook for chronic mesenteric ischemia is good after a successful surgery. However, it is important to make lifestyle changes to prevent hardening of the arteries from getting worse.
People with hardening of the arteries that supply the intestines often have the same problems in blood vessels that supply the heart, brain, kidneys, or legs.
People with acute mesenteric ischemia often do poorly because parts of the intestine may die before surgery can be done. This can be fatal. However, with prompt diagnosis and treatment, acute mesenteric ischemia can be treated successfully.
Possible Complications
Tissue death from lack of blood flow (infarction) in the intestines is the most serious complication of mesenteric artery ischemia. Surgery may be needed to remove the dead portion.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have:
- Changes in bowel habits
- Fever
- Nausea
- Severe abdominal pain
- Vomiting
- Bleeding from the rectum
- Frequent abdominal pain after you eat
Prevention
The following lifestyle changes can reduce your risk for narrowing of the arteries:
- Get regular exercise.
- Follow a healthy diet.
- Get heart rhythm problems treated.
- Keep your blood cholesterol and blood sugar under control.
- Quit smoking.
References
Cameron J. Vascular surgery. In: Cameron J, ed. Current Surgical Therapy. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 16.
Conrad MF. Chronic mesenteric ischemia: epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical evaluation, and management.. In: Sidawy AN, Perler BA, eds. Rutherford's Vascular Surgery and Endovascular Therapy. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 134.
Feuerstadt P, Brandt LJ. Intestinal ischemia. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 118.
Kahi CJ. Vascular diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 129.
Roline CE, Reardon RF. Small intestine. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 78.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 3/31/2024
Reviewed By: Jenifer K. Lehrer, MD, Department of Gastroenterology, Aria - Jefferson Health Torresdale, Jefferson Digestive Diseases Network, Philadelphia, PA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2025 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
