Tooth abscess
Periapical abscess; Dental abscess; Tooth infection; Abscess - tooth; Dentoalveolar abscess; Odontogenic abscess
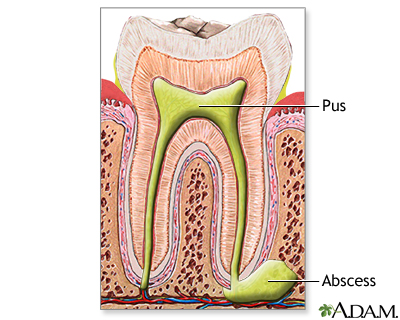
A tooth abscess is a pocket of pus caused by a bacterial infection.
Images
Causes
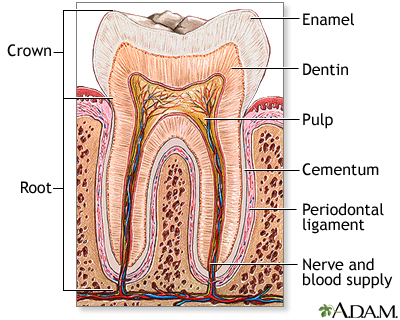
A tooth abscess may form if there is tooth decay. It may also occur when a tooth is broken, chipped, or injured in other ways. Openings in the tooth enamel allow bacteria to infect the center of the tooth (the pulp). Infection may spread from the root of the tooth to the bones supporting the tooth.
Infection results in a buildup of pus and tissue swelling within the tooth. This causes a "toothache". The toothache may stop if pressure is relieved. But the infection will remain active and continue to spread. This will cause more pain and can destroy tissue.
Symptoms
The main symptom is a severe toothache. The pain is continuous. It does not stop. It can be described as gnawing, sharp, shooting, or throbbing.
Other symptoms may include:
- Bitter taste in the mouth
- Breath odor
- General discomfort, uneasiness, or ill-feeling
- Fever
- Pain when chewing
- Sensitivity of the teeth to hot or cold
- Swelling of the gum over the infected tooth, which may look like a pimple
- Swollen glands of the neck
- Swollen area of the upper or lower jaw, which is a very serious symptom
Exams and Tests
Your dentist will closely look at your teeth, mouth, and gums. It may hurt when the dentist taps the tooth. Biting or closing your mouth tightly also increases the pain. Your gums may be swollen and red and may drain thick material.
Dental x-rays and other tests can help your dentist determine which tooth or teeth are causing the problem.
Treatment
The goals of treatment are to cure the infection, save the tooth, and prevent complications.
Your dentist might prescribe antibiotics to fight the infection. Warm saltwater rinses may help ease the pain. Over-the-counter pain relievers may relieve your toothache and fever.
Do not place aspirin directly on your tooth or gums. This increases irritation of the tissues and can result in mouth ulcers.
A root canal may be recommended in an attempt to save the tooth.
If you have a severe infection, your tooth may need to be removed, or you may need surgery to drain the abscess. Some people may need to be admitted to the hospital.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Untreated abscesses may get worse and can lead to life-threatening complications.
Prompt treatment cures the infection in most cases. The tooth can often be saved.
Possible Complications
These complications can occur:
- Loss of the tooth
- Blood infection
- Spread of infection to soft tissue
- Spread of infection to the jaw bone
- Spread of infection to other areas of the body, which can cause brain abscess, inflammation in the heart, pneumonia, or other complications
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your dentist if you have a throbbing toothache that does not go away, or if you notice a bubble (or pimple) on your gums.
Prevention
Prompt treatment of dental decay reduces the risk of developing a tooth abscess. Have your dentist examine any broken or chipped teeth right away.
Related Information
Dental cavitiesToothaches
Cellulitis
Ludwig angina
Osteomyelitis
Brain abscess
Endocarditis
Community-acquired pneumonia in adults
Root canal
References
Hewson I. Dental emergencies. In: Cameron P, Little M, Mitra B, Deasy C, eds. Textbook of Adult Emergency Medicine. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 17.
Pedigo RA Oral medicine. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 56.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 3/31/2024
Reviewed By: Michael Kapner, DDS, General Dentistry, Norwalk Medical Center, Norwalk CT. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2025 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
