Scarlet fever
Scarlatina; Strep infection - scarlet fever; Streptococcus - scarlet fever
Scarlet fever is caused by an infection with bacteria called group A streptococcus. This is the same bacteria that cause strep throat.
Images
I Would Like to Learn About:
Causes
Scarlet fever used to be a severe childhood disease. The group A strep bacteria produce a toxin that causes a distinctive red rash, which led to the name.
The main risk factor for getting scarlet fever is infection with the bacteria that cause strep throat. An outbreak of strep throat or scarlet fever in the community, neighborhood, or school may increase the risk of infection.
Symptoms
The time between infection and symptoms is short, most often 1 to 2 days. The illness will likely begin with a fever and sore throat.
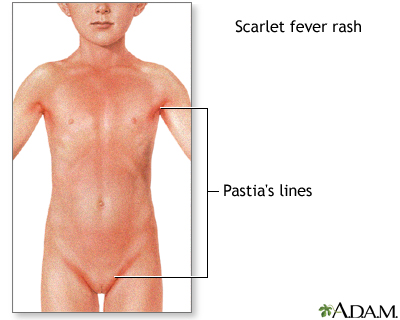
The rash first appears on the neck and chest, then spreads over the body. People say it feels like sandpaper. The texture of the rash is more important than the appearance to confirm the diagnosis. The rash can last for more than a week. As the rash fades, the skin around the fingertips, toes, and groin area may peel.
Other symptoms include:
- Abdominal pain
- Bright red color in the creases of the underarm and groin
- Chills
- Fever
- General discomfort (malaise)
- Headache
- Muscle aches
- Sore throat
- Swollen, red tongue (strawberry tongue)
- Vomiting
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider may check for scarlet fever by doing a:
- Physical examination
- Throat culture that shows bacteria from group A streptococcus
- Throat swab to do a test called rapid antigen detection for group A streptococcus ("rapid strep test")
Treatment
Antibiotics are used to kill the bacteria that cause the throat infection. This is crucial to prevent rheumatic fever, a serious complication of strep throat and scarlet fever.
Outlook (Prognosis)
With proper antibiotic treatment, the symptoms of scarlet fever should get better quickly. However, the rash can last for up to 2 to 3 weeks before it fully goes away.
Possible Complications
Complications are rare with the right treatment, but may include:
- Acute rheumatic fever, which can affect the heart, joints, skin, and brain
- Ear infection
- Kidney damage
- Liver damage
- Pneumonia
- Sinus infection
- Swollen lymph glands or abscess
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if:
- You develop symptoms of scarlet fever
- Your symptoms do not go away 24 hours after beginning antibiotic treatment
- You develop new symptoms
Prevention
Bacteria are spread by direct contact with infected people, or by droplets an infected person coughs or exhales. Avoid contact with infected people.
Related Information
Strep throatRashes
References
Bryant AE, Stevens DL. Streptococcus pyogenes. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 197.
Michaels MG, Williams JV. Infectious diseases. In: Zitelli BJ, McIntire SC, Nowalk AJ, Garrison J, eds. Zitelli and Davis' Atlas of Pediatric Physical Diagnosis. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 13.
Shulman ST, Reuter CH. Group A streptococcus. In: Kliegman RM, St Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 210.
Stevens DL, Bryant AE, Hagman MM. Nonpneumococcal streptococcal infections and rheumatic fever. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 269.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 2/8/2024
Reviewed By: Linda J. Vorvick, MD, Clinical Professor, Department of Family Medicine, UW Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2025 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
