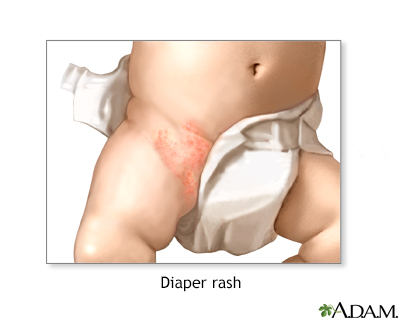
Diaper rash
Dermatitis - diaper and Candida; Candida-associated diaper dermatitis; Diaper dermatitis; Dermatitis - irritant contact
Diaper rash is a skin problem that develops in the area under an infant's diaper.
Images

Causes
Diaper rashes are common in babies from 4 to 15 months old. They may be noticed more when babies begin to eat solid foods.
Diaper rashes caused by infection with a yeast (fungus) called candida are very common in children. Candida grows best in warm, moist places, such as under a diaper. Candida diaper rash is more likely to occur in babies who:
- Are not kept clean and dry
- Are taking antibiotics or whose mothers are taking antibiotics while breastfeeding
- Have more frequent stools
Other causes of diaper rash include:
- Acids in the stool (seen more often when the child has diarrhea)
- Ammonia (a chemical produced when bacteria break down urine)
- Diapers that are too tight or rub the skin
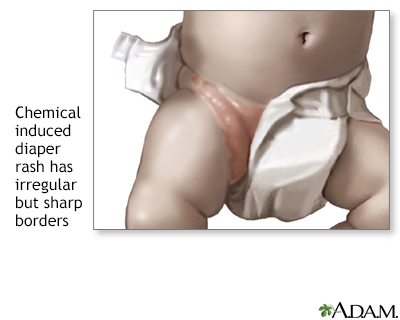
- Reactions to soaps and other products used to clean cloth diapers
Symptoms
You may notice the following in your child's diaper area:
- Bright red rash that gets bigger
- Very red and scaly areas on the scrotum and penis in boys
- Red or scaly areas on the labia and vagina in girls
- Pimples, blisters, ulcers, large bumps, or sores filled with pus
- Smaller red patches (called satellite lesions) that grow and blend in with the other patches
Older infants may scratch when the diaper is removed.
Diaper rashes usually do not spread beyond the edge of the diaper.
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider can often diagnose a yeast diaper rash by looking at your baby's skin. A KOH test can confirm if it is candida.
Treatment
The best treatment for a diaper rash is to keep the skin clean and dry. This also helps prevent new diaper rashes. Lay your baby on a towel without a diaper whenever possible. The more time the baby can be kept out of a diaper, the better.
Other tips include:
- Always wash your hands before and after changing a diaper.
- Change your baby's diaper often and as soon as possible after the baby urinates or passes stool.
- Use water and a soft cloth or cotton ball to gently clean the diaper area with every diaper change. Do not rub or scrub the area. A squirt bottle of water may be used for sensitive areas.
- Pat the area dry or allow to air-dry.
- Put diapers on loosely. Diapers that are too tight do not allow enough air flow and may rub and irritate the baby's waist or thighs.
- Using absorbent diapers helps keep the skin dry and reduces the chance of getting an infection.
- Ask your provider or nurse which creams, ointments, or powders are best to use in the diaper area.
- Ask if a diaper rash cream would be helpful. Zinc oxide or petroleum jelly-based products help keep moisture away from your baby's skin when applied to completely clean, dry skin.
- Do not use wipes that have alcohol or perfume. They may dry out or irritate the skin more.
- Do not use talc (talcum powder). It can get into your baby's lungs.
Certain skin creams and ointments will clear up infections caused by yeast. Nystatin, miconazole, clotrimazole, and ketoconazole are commonly used medicines for yeast diaper rashes. For severe rashes, a steroid ointment, such as 1% hydrocortisone, may be applied. You can buy these without a prescription. But first ask your provider if these medicines will help.
If you use cloth diapers:
- Do not put plastic or rubber pants over the diaper. They do not allow enough air to pass through. Use breathable diaper covers instead.
- Do not use fabric softeners or dryer sheets. They may make the rash worse.
- When washing cloth diapers, rinse 2 or 3 times to remove all soap if your child already has a rash or has had one before.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The rash usually responds well to treatment.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your child's provider if:
- The rash gets worse or does not go away in 2 to 3 days
- The rash spreads to the abdomen, back, arms, or face
- You notice pimples, blisters, ulcers, large bumps, or sores filled with pus
- Your baby also has a fever
- Your baby develops a rash during the first 6 weeks after birth
Related Information
Rash - child under 2 yearsPatches
Rashes
Scrotum
Penis
Vagina
Secondary infections
References
Bender NR, Chiu YE. Eczematous disorders. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 674.
Moon M, Guerrero AM, Li X, Koch E, Gehris RP. Dermatology. In: Zitelli BJ, McIntire SC, Nowalk AJ, Garrison J, eds. Zitelli and Davis' Atlas of Pediatric Physical Diagnosis. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 8.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 8/5/2023
Reviewed By: Neil K. Kaneshiro, MD, MHA, Clinical Professor of Pediatrics, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2025 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
