Croup
Viral croup; Laryngotracheobronchitis; Spasmodic croup; Barking cough; Laryngotracheitis
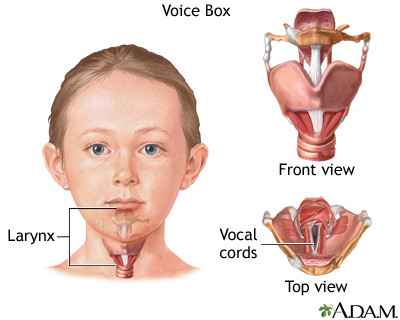
Croup is an infection of the upper airways that causes breathing difficulty and a barking cough. Croup is due to swelling around the vocal cords. It is common in infants and children.
Images
I Would Like to Learn About:
Causes
Croup affects children ages 3 months to 5 years. It can occur at any age. Some children are more likely to get croup and may get it several times. It is most common between October and April, but can occur at any time of the year.
Croup is most often caused by viruses such as parainfluenza RSV, measles, adenovirus, and influenza. More severe cases of croup may be caused by bacteria. This condition is called bacterial tracheitis.
Croup-like symptoms may also be caused by:
- Allergies
- Breathing in something that irritates your airway
- Acid reflux
Symptoms
The main symptom of croup is a cough that sounds like a seal barking.
Most children will have a mild cold and a low grade fever for several days before having barking cough and a hoarse voice. As the cough gets more frequent, the child may have trouble breathing or stridor (a harsh, crowing noise made when breathing in).
Croup is typically much worse at night. It often lasts 3 to 7 nights. The first night or two are most often the worst. Rarely, croup can last for weeks. Talk to your child's health care provider if croup lasts longer than a week or comes back often.
Exams and Tests
Your provider will take a medical history and ask about your child's symptoms. Your provider will examine your child's chest to check for:
- Difficulty breathing in and out
- Whistling sound (wheezing)
- Decreased breath sounds
- Chest retractions with breathing
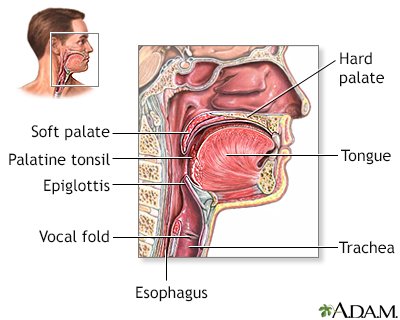
An exam of the throat may reveal a red epiglottis. In a few cases, x-rays or other tests may be needed.
A neck x-ray may reveal a foreign object or narrowing of the trachea.
Treatment
Most cases of croup can be safely managed at home with telephone support from your provider. However, if you are worried about your child's symptoms, you should call your provider for advice, even in the middle of the night.
Steps you can take at home include:
- Expose your child to cool or moist air, such as in a steamy bathroom or outside in the cool night air. This may offer some breathing relief.
- Set up a cool air vaporizer in the child's bedroom and use it for a few nights.
- Make your child more comfortable by giving acetaminophen. This medicine also lowers a fever so the child will not have to breathe as hard.
- Avoid cough medicines unless you discuss them with your provider first.
Your provider may prescribe medicines, such as:
- Steroid medicines taken by mouth or through an inhaler
- Antibiotic medicine (for some, but not most cases)
Your child may need to be treated in the emergency room or to stay in the hospital if they:
- Have breathing problems that do not go away or get worse
- Become too tired because of breathing problems
- Have bluish skin color
- Are not drinking enough fluids
Medicines and treatments used at the hospital may include:
- Breathing medicines given with a nebulizer machine
- Steroid medicines given through a vein (IV)
- An oxygen tent placed over a crib
- Fluids given through a vein for dehydration
- Antibiotics given through a vein
Rarely, a breathing tube through the nose or mouth will be needed to help your child breathe.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Croup is most often mild, but it can still be dangerous. It most often goes away in 3 to 7 days.
In some severe cases of croup that does not require emergency department care, a short course of oral glucocorticoids (steroids) may be useful to reduce swelling and improve symptoms.
The tissue that covers the trachea (windpipe) is called the epiglottis. If the epiglottis becomes infected, the entire windpipe can swell shut. This is a life-threatening condition.
If an airway blockage is not treated promptly, the child can have severe trouble breathing or breathing may stop completely.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if your child is not responding to home treatment or is acting more irritable.
Call 911 or the local emergency number right away if:
- Croup symptoms may have been caused by an insect sting or inhaled object.
- Your child has bluish lips or skin color.
- Your child is drooling.
- Your child is having trouble swallowing.
- There is stridor (a noise when breathing in).
- There is a tugging-in of the muscles between the ribs when breathing in.
- Your child is struggling to breathe.
Prevention
Some of the steps to be taken to prevent infection are:
- Wash your hands frequently and avoid close contact with people who have a respiratory infection.
- Timely immunizations with the diphtheria, Haemophilus influenzae (Hib), and measles vaccines protect children from some of the most dangerous forms of croup.
Related Information
Breathing difficultyEpiglottitis
Breathing - slowed or stopped
Atelectasis
References
Aregbesola A, Tam CM, Kothari A, Le ML, Ragheb M, Klassen TP. Glucocorticoids for croup in children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023;1(1):CD001955. PMID: 36626194 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36626194/.
Chi DH, Tobey A. Otolaryngology. In: Zitelli BJ, McIntire SC, Nowalk AJ, Garrison J, eds. Zitelli and Davis' Atlas of Pediatric Physical Diagnosis. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 24.
Cai Y, Meyer A. Pediatric infectious disease. In: Flint PW, Francis HW, Haughey BH, et al, eds. Cummings Otolaryngology: Head and Neck Surgery. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 201.
James P, Hanna S. Upper airway obstruction in children. In: Bersten AD, Handy JM, eds. Oh's Intensive Care Manual. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 106.
Rodrigues KK, Roosevelt GE. Acute inflammatory upper airway obstruction (croup, epiglottitis, laryngitis, and bacterial tracheitis). In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 412.
Rose E. Pediatric respiratory emergencies: upper airway obstruction and infections. In: Walls RM, Hockberger RS, Gausche-Hill M, eds. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 167.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 2/17/2024
Reviewed By: Charles I. Schwartz, MD, FAAP, Clinical Assistant Professor of Pediatrics, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, General Pediatrician at PennCare for Kids, Phoenixville, PA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2025 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
