Impetigo
Streptococcus - impetigo; Strep - impetigo; Staph - impetigo; Staphylococcus - impetigo
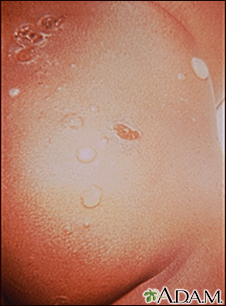
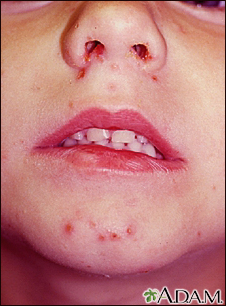
Impetigo is a common infection of the outermost layer of the skin.
Images
I Would Like to Learn About:
Causes
Impetigo is caused by streptococcus (strep) or staphylococcus (staph) bacteria. Methicillin-resistant staph aureus (MRSA) is an increasing cause.
Skin typically has many types of bacteria on it. When there is a break in the skin, bacteria can enter the body and grow there. This causes inflammation and infection. Breaks in the skin may occur from injury or trauma to the skin or from insect, animal, or human bites.
Impetigo may also occur on the skin, where there is no visible break.
Impetigo is most common in children who live in unhealthy conditions.
In adults, it may occur following another skin problem. It may also develop after a cold or other virus.
Impetigo can spread to others. You can catch the infection from someone who has it if the fluid that oozes from their skin blisters touches an open area on your skin.
Symptoms
Symptoms of impetigo are:
- One or many blisters that are filled with pus and easy to pop. In infants, the skin is reddish or raw-looking where a blister has broken.
- Blisters that itch are filled with yellow or honey-colored fluid and ooze and crust over. Rash that may begin as a single spot but spreads to other areas due to scratching.
- Skin sores on the face, lips, arms, or legs that spread to other areas.
- Swollen lymph nodes near the infection.
- Patches of impetigo on the body (in children).
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will look at your skin to determine if you have impetigo.
Your provider may take a sample of bacteria from your skin to grow in the lab. This can help determine if MRSA is the cause. Specific antibiotics are needed to treat this type of bacteria.
Treatment
The goal of treatment is to get rid of the infection and relieve your symptoms.
Your provider will prescribe an antibacterial cream. You may need to take antibiotics by mouth if the infection is severe.
Gently wash (do not scrub) your skin several times a day. Use an antibacterial soap to remove crusts and drainage.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The sores of impetigo heal slowly. Scars are rare. The cure rate is very high, but the problem often comes back in young children.
Possible Complications
Impetigo may lead to:
- Spread of the infection to other parts of the body (common)
- Kidney inflammation or failure (rare)
- Permanent skin damage and scarring (very rare)
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have symptoms of impetigo.
Prevention
Prevent the spread of infection.
- If you have impetigo, always use a clean washcloth and towel each time you wash.
- Do not share towels, clothing, razors, and other personal care products with anyone.
- Avoid touching blisters that are oozing.
- Wash your hands thoroughly after touching infected skin.
Keep your skin clean to prevent getting the infection. Wash minor cuts and scrapes well with soap and clean water. You can use a mild antibacterial soap.
Related Information
RashesCellulitis
Vesicles
Ulcers
Systemic
Acute kidney failure
Glomerulonephritis
References
Dinulos JGH. Bacterial infections. In: Dinulos JGH, ed. Habif's Clinical Dermatology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 9.
Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al. Cutaneous bacterial infections. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 706.
McLarney RM, Sommer LL, Reboli AC, Heymann WR. Bacterial diseases. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 74.
Pasternack MS, Swartz MN. Cellulitis, necrotizing fasciitis, and subcutaneous tissue infections. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 93.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 10/13/2024
Reviewed By: Ramin Fathi, MD, FAAD, Director, Phoenix Surgical Dermatology Group, Phoenix, AZ. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2025 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
