Anaphylaxis
Anaphylactic reaction; Anaphylactic shock; Shock - anaphylactic; Allergic reaction - anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis is a life-threatening type of allergic reaction.
Images


Causes
Anaphylaxis is a severe, whole-body allergic reaction to a chemical that has become an allergen. An allergen is a substance that, for most people, is harmless, but in some people, it can cause an allergic reaction.
After being exposed to a substance such as bee sting venom, the person's immune system becomes sensitized to it. When the person is exposed to that allergen again, an allergic reaction may occur. Anaphylaxis usually happens quickly after the exposure. The condition is severe and involves the whole body.
Tissues in different parts of the body release histamine and other substances. This causes the airways to tighten and leads to other symptoms.
Some medicines (morphine, x-ray dye, aspirin, and others) may cause an anaphylactic-like reaction (often called an anaphylactoid reaction) when people are first exposed to them. These reactions are not the same as the immune system response that occurs with true anaphylaxis. But, the symptoms, risk of complications, and treatment are the same for both types of reactions.
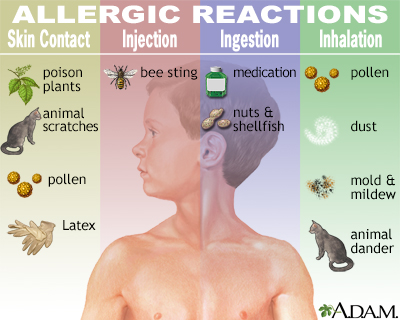
Anaphylaxis can occur in response to any allergen. Common causes include:
Pollen and other inhaled allergens rarely cause anaphylaxis. Some people have an anaphylactic reaction with no known cause.
Anaphylaxis is life threatening and can occur at any time. Risks include a history of any type of allergic reaction.
Symptoms
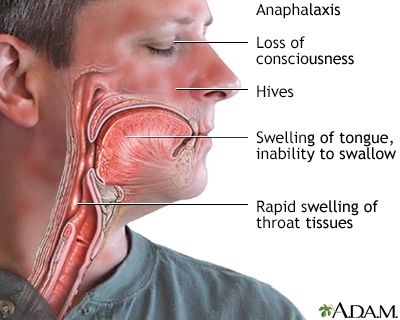
Symptoms develop quickly, often within seconds or minutes. They may include any of the following:
- Abdominal pain
- Feeling anxious
- Chest discomfort or tightness
- Diarrhea
- Difficulty breathing, coughing, wheezing, or high-pitched breathing sounds
- Difficulty swallowing
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
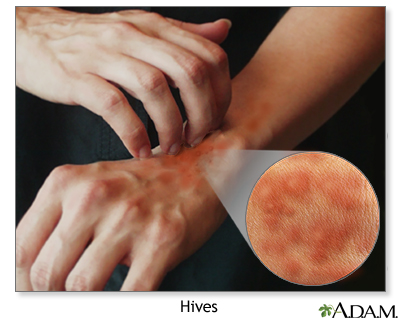
- Hives, itchiness, redness of the skin
- Nasal congestion
- Nausea or vomiting
- Palpitations
- Slurred speech
- Swelling of the face, eyes, or tongue
- Unconsciousness
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will examine the person and ask about what might have caused the condition.
Tests for the allergen that caused anaphylaxis (if the cause is not obvious) may be done after treatment.
Treatment
Anaphylaxis is an emergency condition that needs medical attention right away. Call 911 or the local emergency number immediately.
Check the person's airway, breathing, and circulation, which are known as the ABC's of Basic Life Support. A warning sign of dangerous throat swelling is a very hoarse or whispered voice, or coarse sounds when the person is breathing in air. If necessary, begin rescue breathing and CPR.
- Call 911 or the local emergency number.
- Calm and reassure the person.
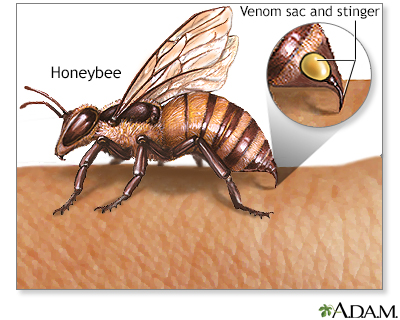
- If the allergic reaction is from a bee sting, scrape the stinger off the skin with something firm (such as a fingernail or plastic credit card). Do not use tweezers. Squeezing the stinger will release more venom.
- If the person has emergency allergy medicine on hand, help them take or inject it. Do not give medicine by the mouth if the person is having difficulty breathing. An epinephrine injector should be used immediately if it is available.
- Take steps to prevent shock. Have the person lie flat, raise the person's feet about 12 inches (30 centimeters), and cover the person with a coat or blanket. Do not place the person in this position if a head, neck, back, or leg injury is suspected, or if it causes discomfort.
DO NOT:
- Do not assume that any allergy shots the person has already received will provide complete protection.
- Do not place a pillow under the person's head if they are having trouble breathing. This can block the airways.
- Do not give the person anything by mouth if they are having trouble breathing.
Paramedics or other providers may place a tube through the nose or mouth into the airways. Or emergency surgery will be done to place a tube directly into the trachea.
The person may receive medicines to further reduce symptoms.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Anaphylaxis can be life threatening without prompt treatment. Symptoms usually do get better with the right therapy, so it is important to act right away.
Possible Complications
Without prompt treatment, anaphylaxis may result in:
- Blocked airway
- Cardiac arrest (no effective heartbeat)
- Respiratory arrest (no breathing)
- Shock
- Death
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call 911 or the local emergency number if you or someone you know develops severe symptoms of anaphylaxis. Or, go to the nearest emergency room.
Prevention
To prevent allergic reactions and anaphylaxis:
- Avoid triggers such as foods and medicines that have caused an allergic reaction in the past. Ask detailed questions about ingredients when you are eating away from home. Also carefully examine ingredient labels.
- If you have a child who is allergic to certain foods, introduce one new food at a time in small amounts so you can recognize an allergic reaction.
- People who know that they have had serious allergic reactions should wear a medical ID tag or bracelet.
- If you have a history of serious allergic reactions, carry injectable epinephrine according to your provider's instructions.
- There is no contraindication to using epinephrine in a severe allergic reaction.
Related Information
Allergic reactionsWheezing
Breathing difficulty
Shock
Pulmonary edema
Hives
Angioedema
Arrhythmias
Insect bites and stings
Food allergy
Drug allergies
Breathing - slowed or stopped
References
Barksdale AN, Ross W. Allergy, anaphylaxis, and angioedema. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 106.
Dreskin SC, Stitt JM. Anaphylaxis. In: Burks AW, Holgate ST, O'Hehir RE, et al, eds. Middleton's Allergy: Principles and Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 75.
Schwartz LB, Castells M. Anaphylaxis. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 233.
Shaker MS, Wallace DV, Golden DBK, et al. Anaphylaxis-a 2020 practice parameter update, systematic review, and Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) analysis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020;145(4):1082-1123. PMID: 32001253 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32001253/.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 3/31/2024
Reviewed By: Deborah Pedersen, MD, MS, Allergy & Asthma Care, PC, Taunton, MA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2025 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
