Congenital antithrombin III deficiency
Deficiency - antithrombin III - congenital; Antithrombin III deficiency - congenital
Congenital antithrombin III (three) deficiency is a genetic disorder that causes the blood to clot more than normal.
Images
I Would Like to Learn About:
Causes
Antithrombin III is a protein in the blood that blocks blood clots from forming. It helps the body keep a healthy balance between bleeding and clotting. Congenital antithrombin III deficiency is an inherited disease. It occurs when a person receives one variant copy of the antithrombin III gene from a parent with the disease.
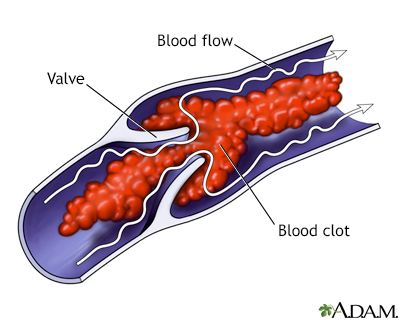
The variant gene leads to a low level of the antithrombin III protein. This low level of antithrombin III can cause blood clots (thrombi) that can block blood flow and damage organs.
People with this condition will often have blood clots at a young age for no reason. They are also likely to have family members who have had a blood clotting problem.
Symptoms
People will usually have symptoms of a blood clot. Blood clots in the arms or legs usually cause swelling, redness, and pain. When a blood clot breaks off from where it formed and travels to another part of the body, it is called a thromboembolism. Symptoms depend on where the blood clot travels to. A common place is the lung, where the clot can cause a cough, shortness of breath, pain while taking deep breaths, chest pain, and even death. Blood clots that travel to the brain can cause a stroke.
Exams and Tests
A physical exam may show:
- A swollen leg or arm
- Decreased breath sounds in the lungs
- A rapid heart rate
Your health care provider can also order a blood test to check if you have a low level of antithrombin III.
Treatment
A blood clot is treated with blood-thinning medicines (also called anticoagulants). How long you need to take these medicines depends on how serious the blood clot was and other factors. Discuss this with your provider.
Support Groups
More information and support for people with congenital antithrombin III deficiency and their families can be found at:
- National Organization for Rare Disorders -- rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/antithrombin-deficiency/
- MedlinePlus -- medlineplus.gov/genetics/condition/hereditary-antithrombin-deficiency/
- National Blood Clot Alliance -- www.stoptheclot.org/programs-services/
Outlook (Prognosis)
Most people have a good outcome if they stay on anticoagulant medicines.
Possible Complications
Blood clots can cause death. Blood clots in the lungs are very dangerous.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
See your provider if you have symptoms of this condition.
Prevention
Once a person is diagnosed with antithrombin III deficiency, all close family members should be screened for this disorder. Blood-thinning medicines can prevent blood clots from forming and prevent complications from clotting.
Related Information
Antithrombin III blood testProtein in diet
Blood clots
References
Anderson JAM, Weitz JI. Hypercoagulable states. In: Hoffman R, Benz EJ, Silberstein LE, et al, eds. Hematology: Basic Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 138.
Schafer AI. Thrombotic disorders: hypercoagulable states. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 67.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 2/3/2025
Reviewed By: Warren Brenner, MD, Oncologist, Lynn Cancer Institute, Boca Raton, FL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2025 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
