Osteoporosis
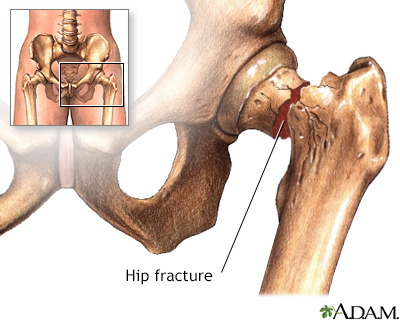
Thin bones; Low bone density; Metabolic bone disease; Hip fracture - osteoporosis; Compression fracture - osteoporosis; Wrist fracture - osteoporosis
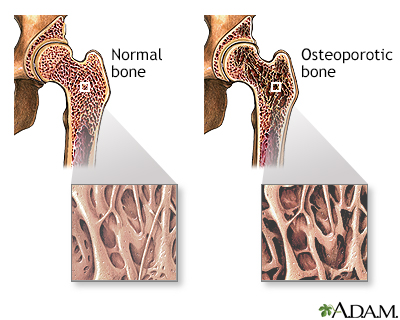
Osteoporosis is a disease in which bones become fragile and more likely to break (fracture).
Images


Animation


I Would Like to Learn About:
Causes
Osteoporosis is the most common type of bone disease.
Osteoporosis increases the risk for breaking a bone. About one half of all women over the age of 50 will have a fracture of the hip, wrist, or vertebrae (bones of the spine) during their lifetime. Spine fractures are the most common.
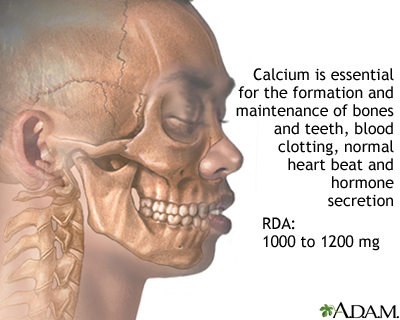
Your body needs the minerals calcium and phosphate to make and keep healthy bones.
- During your life, your body continues to both reabsorb old bone and create new bone.
- As long as your body has a good balance of new and old bone, your bones stay healthy and strong.
- Bone loss occurs when more old bone is reabsorbed than new bone is created.
Sometimes, bone loss occurs without any known cause. Other times, bone loss and thin bones run in families. In general, white, older women are the most likely to have bone loss.
Brittle, fragile bones can be caused by anything that makes your body reabsorb too much bone, or keeps your body from making enough new bone. As you age, your body may reabsorb calcium and phosphate from your bones instead of keeping these minerals in your bones. This makes your bones weaker.
A major risk factor is not consuming enough calcium to build new bone tissue. It is important to eat/drink enough high-calcium foods. You also need vitamin D, because it helps your body absorb calcium. Your bones may become brittle and more likely to fracture if:
- If you do not eat enough food with calcium and vitamin D
- Your body does not absorb enough calcium and vitamin D from your food, such as after gastric bypass surgery or due to other medical conditions
Other causes of bone loss include:
- A decrease in estrogen in women at the time of menopause and a decrease in testosterone in men as they age
- Being confined to a bed due to a prolonged illness (mostly affects bones in children)
- Having certain medical conditions that cause increased inflammation in the body such as Crohn disease or rheumatoid arthritis
- Taking certain medicines, such as certain seizure medicines, hormone treatments for prostate or breast cancer, and steroid medicines taken for more than 3 months
Other risk factors include:
- Absence of menstrual periods for long periods of time
- A family history of osteoporosis
- Drinking a large amount of alcohol
- Low body weight
- Smoking
- Having an eating disorder, such as anorexia nervosa
- Certain ethnic groups have a higher rate of low bone mass
Symptoms
There are no symptoms in the early stages of osteoporosis. Many times, people will have a fracture before learning they have the disease.
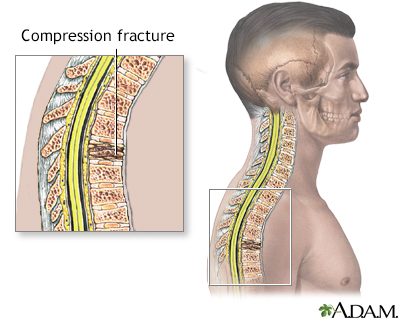
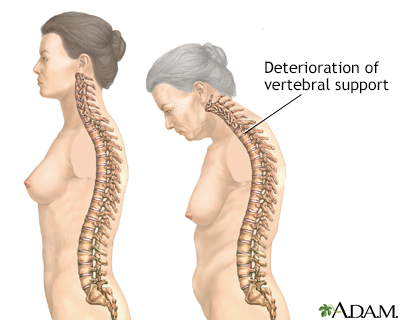
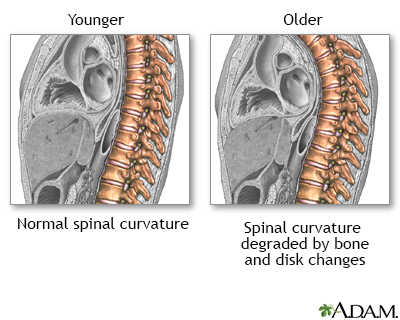
Fractures of the bones of the spine can cause pain almost anywhere in the spine. These are called compression fractures. They often occur without an injury. The pain may occur suddenly or slowly over time.
There can be a loss of height (as much as 6 inches or 15 centimeters) over time. A stooped posture or a condition called a dowager's hump may develop.
Exams and Tests
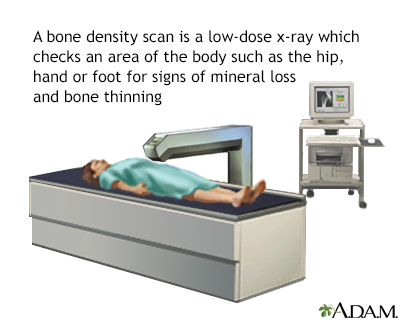
A DEXA scan is a low-radiation x-ray that measures the density of the minerals in your bones. Most often, it measures density in the spine and hip bones. Your health care provider uses this test to:
- Diagnose bone loss and osteoporosis.
- Predict your risk for future bone fractures.
- See how well an osteoporosis medicine is working. (For this purpose, the DEXA scan is most often repeated every 2 years or longer.)
The US Preventive Services Task Force recommends this screening test at least once for women age 65 and older, and for some women younger than age 65 who have an increased risk for osteoporosis. So far, research does not show a need for repeating screening after the test at age 65.
A simple spine or hip x-ray may show fracture or collapse of the spinal bones. However, simple x-rays of other bones are not very accurate in predicting whether you are likely to have osteoporosis. A low-radiation spine x-ray called a vertebral fracture assessment (VFA) can be done with a DEXA to better identify fractures that do not have any symptoms. Trabecular bone score (TBS) can also be performed to gauge bone quality and help evaluate fracture risk.
You may need blood and urine tests if your provider thinks the cause of your osteoporosis is a medical condition, rather than the slow bone loss that occurs with aging.
DEXA scan results compare your bone mineral density with both a young adult who has no bone loss and with people your age and sex. This means that at age 80, almost one third of women with normal age-related bone loss would have osteoporosis, based on their DEXA scan results.
Treatment
Treatment for osteoporosis may involve:
- Making lifestyle changes, such as changing your diet and exercise routine and stopping tobacco or alcohol use
- Taking calcium and vitamin D supplements
- Using medicines
Medicines may be used to strengthen bones when:
- Osteoporosis has been diagnosed by a bone density study, whether or not you have a fracture, and your fracture risk is high.
- You have had a bone fracture, and a bone density test shows that you have thin bones, but not osteoporosis.
Medicines used to treat osteoporosis include:
- Bisphosphonates -- the main medicines used to prevent and treat osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. They can be given by mouth or by intravenous (IV) injection.
- Denosumab -- lessens bone loss and increases bone density. Given by injection under the skin.
- Teriparatide or abaloparatide -- man-made forms of a hormone your body makes that increases bone density.
- Romosozumab -- a newer medicine for more severe bone thinning.
- Estrogen receptor modulators such as raloxifene.
- Calcitonin -- a man-made form of a hormone your body makes that increases bone density. Used mainly to treat the acute pain from a spine compression fracture.
The length of time a woman should take these medicines depends on her level of risk. Recommendations include:
- Low fracture risk -- 5 years of oral medicine or 3 years of IV therapy
- High fracture risk -- 10 years of oral medicine or 6 years of IV therapy
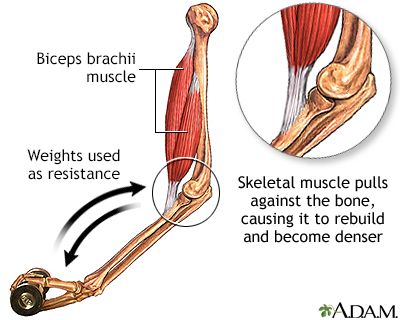
Exercise plays a key role in preserving bone density in older adults. Some of the exercises recommended to reduce your chance of a fracture include:
- Weight-bearing exercises, such as walking, jogging, playing tennis, or dancing for at least 30 minutes, three times per week
- Free weights, weight machines, stretch bands
- Balance exercises, that may include tai chi and yoga
- Rowing machines
Avoid any exercise that presents a risk of falling. Also, do not do high-impact exercises that can cause fractures in older adults.
Follow these guidelines for getting enough calcium and vitamin D:
- Adults age 50 and under should have 1,000 mg of calcium and 400 to 800 International Units (IU) of vitamin D a day.
- Women ages 51 to 70 should have 1,200 mg of calcium and 400 to 800 IU of vitamin D a day.
- Men ages 51 to 70 should have 1,000 mg of calcium and 400 to 800 IU of vitamin D a day.
- Adults over age 70 should have 1,200 mg of calcium and 800 IU of vitamin D a day.
- Your provider may recommend a calcium supplement.
- Follow a diet that provides the proper amount of calcium and vitamin D. Use supplements to make up for the shortage only if your diet does not have the recommended amounts.
- Your provider may recommend higher doses of vitamin D if you have risk factors for osteoporosis or a low level of this vitamin.
(Note: Some expert groups are not sure the benefits and safety of these amounts of vitamin D and calcium outweigh their risks. Be sure to discuss with your provider whether supplements are a good choice for you.)
Stop unhealthy habits:
- Quit smoking, if you smoke.
- Limit your alcohol intake. Too much alcohol can damage your bones. Alcohol consumption also puts you at risk for falling and breaking a bone.
It is important to prevent falls by older people. These suggestions can help:
- Do not take medicines that make you drowsy or unsteady. If you must take them, be extra careful when you are up and moving around. For example, hold on to countertops or sturdy furniture to avoid falling.
- Remove household hazards, such as throw rugs, to reduce the risk for falls.
- Leave lights on at night so you can see better when walking around your house.
- Install and use safety grab bars in the bathroom.
- Install antislip flooring in bathtubs and showers.
- Make sure your vision is good. Have your eyes checked once a year by an eye doctor or more often if you notice changes in your vision.
- Wear shoes that fit well and have low heels. This includes slippers. Slippers that do not have heels can cause you to trip and fall.
- Do not walk outdoors alone on icy days.
Surgery to treat severe, disabling pain from spinal fractures due to osteoporosis includes:
- Kyphoplasty (a material is placed into a bone of your spine to restore the height of the vertebrae)
- Spinal fusion (bones of your spine are joined together so they do not move against each other)
Outlook (Prognosis)
Medicines to treat osteoporosis can help prevent future fractures. Spine bones that have already collapsed can't be made stronger.
Osteoporosis can cause a person to become disabled from weakened bones. Hip fractures are one of the main reasons people are admitted to nursing homes.
Prevention
Be sure you get enough calcium and vitamin D to build and maintain healthy bones. Following a healthy, well-balanced diet can help you get these and other important nutrients.
Other tips for prevention:
- Do not drink large amounts of alcohol.
- Do not smoke.
- Get regular exercise.
Medicines can treat osteoporosis and prevent fractures. Your provider can tell you if any are right for you.
Related Information
MenopauseCushing syndrome
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperparathyroidism
Bulimia
Hip fracture surgery
Hip fracture - discharge
Preventing falls
References
De Paula FJA, Black DM, Miller PD, Rosen CJ. Osteoporosis: basic and clinical aspects. In: Melmed S, Auchus, RJ, Goldfine AB, Rosen CJ, Kopp PA, eds. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. 15th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 29.
LeBoff MS, Greenspan SL, Insogna KL, et al. The clinician's guide to prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int. 2022; 33(10):2049-2102. PMID: 35478046 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35478046/.
Reid IR, Billington EO. Osteoporosis. In: Robertson RP, ed. DeGroot's Endocrinology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 60.
Shoback D, Rosen CJ, Black DM, Cheung AM, Murad MH, Eastell R. Pharmacological management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women: an Endocrine Society guideline update. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020;105(3):587-594. PMID: 32068863 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32068863/.
US Preventive Services Task Force, Grossman DC, Curry SJ, Owens DK, et al. Vitamin D, calcium, or combined supplementation for the primary prevention of fractures in community-dwelling adults: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA. 2018;319(15):1592-1599. PMID: 29677309 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29677309/.
US Preventive Services Task Force website. Osteoporosis to prevent fractures: screening. www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/recommendation/osteoporosis-screening. Published January 14, 2025. Accessed February 12, 2025.
Weber TJ. Osteoporosis. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 225.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 1/28/2025
Reviewed By: Diane M. Horowitz, MD, Rheumatology and Internal Medicine, Northwell Health, Great Neck, NY. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2025 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
