Solitary pulmonary nodule
Lung cancer - solitary nodule; Infectious granuloma - pulmonary nodule; SPN
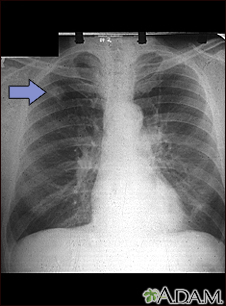
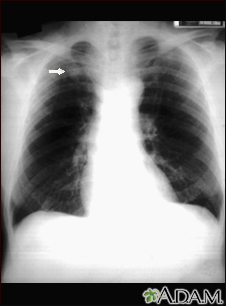
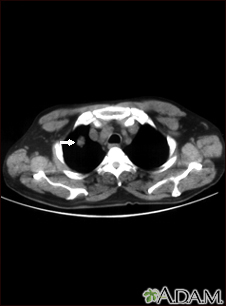
A solitary pulmonary nodule is a round or oval spot (lesion) in the lung that is seen with a chest x-ray or CT scan.
Images
Causes
More than half of all solitary pulmonary nodules are noncancerous (benign). Benign nodules have many causes, including scars and past infections.
Infectious granulomas (which are formed by cells as a reaction to a past infection) cause most benign nodules. Common infections that often result in granulomas or other healed scars include:
- Tuberculosis (TB) or exposure to TB
- Fungus, such as aspergillosis, coccidioidomycosis, cryptococcosis, or histoplasmosis
Primary lung cancer is the most common cause of cancerous (malignant) pulmonary nodules. This is cancer that starts in the lung.
Symptoms
A solitary pulmonary nodule itself rarely causes symptoms.
Exams and Tests
A solitary pulmonary nodule is most often found on a chest x-ray or chest CT scan. These imaging tests are often done for other symptoms or reasons. It can also occur as part of the screening chest CT for people age 50 to 80 years who have a 20 pack-year smoking history.
Your health care provider must decide whether the nodule in your lung is most likely benign or of concern. A nodule more is likely benign if:
- The nodule is small, has a smooth border, and has a solid and even appearance on an x-ray or CT scan.
- You are young and never smoked.
Your provider may then choose to monitor the nodule over time by repeating a series of x-rays or CT scans.
- Repeat chest x-rays or chest CT scans are the most common way to monitor the nodule. Sometimes, lung PET scans may be done.
- If repeated x-rays show that the nodule size has not changed in 2 years, it is most likely benign and a biopsy is not needed.
Your provider may recommend a biopsy of the nodule to check for cancer if:
- You are a smoker.
- You have other symptoms of lung cancer.
- The nodule has grown in size or has changed when compared to earlier images.
- The nodule has features that make it more likely to be cancerous (malignant).
A lung needle biopsy may be done by placing a needle directly through the wall of your chest, or during procedures called bronchoscopy or mediastinoscopy.
Tests to check for TB and other infections may also be done.
Treatment
Ask your provider about the risks of having a biopsy versus monitoring the size of the nodule with regular x-rays or CT scans. Treatment may be based on the results of the biopsy or other tests.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The outlook is usually good if the nodule is benign. If the nodule does not grow larger over a 2-year period, often nothing more needs to be done.
Related Information
Chest x-raySkin nodules
Benign
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis
Lung cancer - small cell
Pulmonary tuberculosis
Histoplasmosis
Valley fever
References
Bueno J, Landeras L, Chung JH. Updated Fleischner Society guidelines for managing incidental pulmonary nodules: common questions and challenging scenarios. Radiographics. 2018;38(5):1337-1350. PMID: 30207935 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30207935/.
Jokerst CE, Gotway MB. Thoracic radiology: noninvasive diagnostic imaging. In: Broaddus VC, Ernst JD, King TE, et al, eds. Murray and Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 20.
Reed JC. Solitary pulmonary nodule. In: Reed JC, ed. Chest Radiology: Patterns and Differential Diagnoses. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 20.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 8/13/2023
Reviewed By: Denis Hadjiliadis, MD, MHS, Paul F. Harron Jr. Professor of Medicine, Pulmonary, Allergy, and Critical Care, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2025 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
