Head injury - first aid
Brain injury; Head trauma; Concussion - head injury; Traumatic - head injury
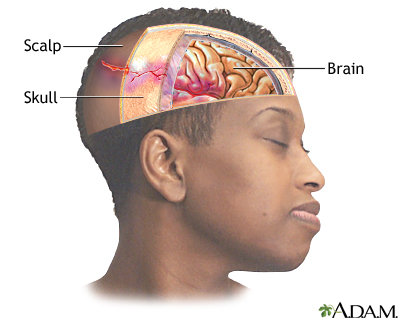
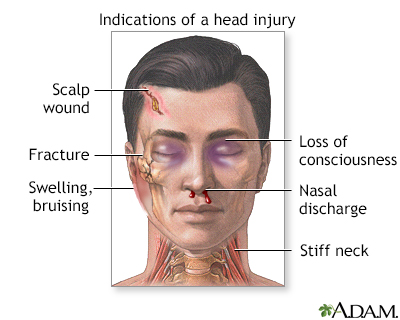
A head injury is any trauma to the scalp, skull, or brain.
Head injury can be either closed or open (penetrating).
- A closed head injury means you received a hard blow to the head from striking an object, but the object did not penetrate the skull.
- An open, or penetrating, head injury means you were hit with an object that broke the skull and entered the brain. This is more likely to happen when you move at a high speed, such as going through the windshield during a car accident. It can also happen from a gunshot to the head.
Head injuries include:
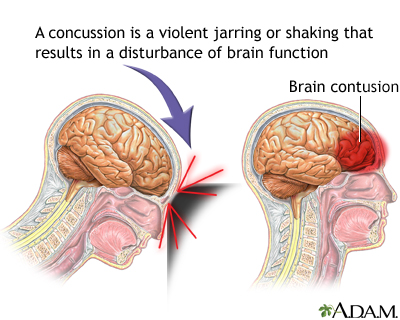
- Concussion, most often in which the brain has been shaken, is the most common type of traumatic brain injury.
- Scalp wounds.
- Skull fractures.
Head injuries may cause bleeding:
- In the brain tissue
- In the layers that surround the brain (subarachnoid hemorrhage, subdural hematoma, epidural hematoma)
Head injury is a common reason for an emergency room visit. A large number of people who suffer head injuries are children. Each year an estimated 1.5 million Americans sustain a traumatic brain injury (TBI). As a consequence of these injuries, 230,000 people are hospitalized and survive.
Images

I Would Like to Learn About:
Causes
Common causes of head injury include:
- Accidents at home, work, outdoors, or while playing sports
- Falls
- Physical assault
- Traffic accidents
Most of these injuries are minor because the skull protects the brain. Some injuries are severe enough to require a stay in the hospital.
Symptoms
Head injuries may cause bleeding in the brain tissue and the layers that surround the brain (subarachnoid hemorrhage, subdural hematoma, epidural hematoma).
Symptoms of a head injury can occur right away or may develop slowly over several hours or days. Even if the skull is not fractured, the brain can hit the inside of the skull and be bruised. The head may look fine, but problems could result from bleeding or swelling inside the skull.
The spinal cord is also likely to be injured from falls from a significant height or ejection from a vehicle.
Some head injuries cause changes in brain function. This is called a traumatic brain injury. A concussion is a type of traumatic brain injury. Symptoms of a concussion can range from mild to severe.
First Aid
Learning to recognize a serious head injury and give basic first aid can save someone's life. For a moderate to severe head injury, call 911 or the local emergency number right away.
Get medical help right away if the person:
- Becomes very sleepy
- Behaves abnormally, or has speech that does not make sense
- Develops a severe headache or stiff neck
- Has a seizure
- Has pupils (the dark central part of the eye) of unequal sizes
- Is unable to move all or part of an arm or leg
- Loses consciousness, even briefly
- Vomits more than once
Then take the following steps:
- Check the person's airway, breathing, and circulation. If necessary, begin rescue breathing and CPR.
- If the person's breathing and heart rate are normal, but the person is unconscious, treat as if there is a spinal injury. Stabilize the head and neck by placing your hands on both sides of the person's head. Keep the head in line with the spine and prevent movement. Wait for medical help.
- Stop any bleeding by firmly pressing a clean cloth on the wound, unless you suspect a skull fracture. If the injury is serious, be careful not to move the person's head. If blood soaks through the cloth, do not remove it. Place another cloth over the first one.
- If you suspect a skull fracture, do not apply direct pressure to the bleeding site, and do not remove any debris from the wound. Cover the wound with sterile gauze dressing.
- If the person is vomiting or about to vomit, to prevent choking, roll the person's head, neck, and body as one unit while stabilizing the head and neck onto their side. This still protects the spine, which you must always assume is injured in the case of a head injury. Children often vomit once after a head injury. This may not be a problem, but contact your health care provider for further guidance.
- Apply ice packs to swollen areas (cover ice in a towel so it does not directly touch the skin).
Do Not
Follow these precautions:
- Do not wash a head wound that is deep or bleeding a lot.
- Do not remove any object sticking out of a wound.
- Do not move the person unless absolutely necessary.
- Do not shake the person if they seem dazed.
- Do not remove a helmet if you suspect a serious head injury.
- Do not pick up a fallen child with any sign of head injury.
- Do not drink alcohol or use illicit drugs within 48 hours of a serious head injury.
A serious head injury that involves bleeding or brain damage must be treated in a hospital.
For a mild head injury, no treatment may be needed. However, contact your provider for medical advice and watch for symptoms of a head injury, which can show up later.
Your provider will explain what to expect, how to manage any headaches, how to treat your other symptoms, when to return to sports, school, work, and other activities, and signs or symptoms to worry about.
- Children will need to be watched and make activity changes.
- Adults also need close observation and activity changes.
Both adults and children must follow their provider's instructions about when it will be possible to return to sports.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call 911 or the local emergency number right away if:
- There is severe head or face bleeding.
- The person is confused, tired, or unconscious.
- The person stops breathing.
- You suspect a serious head or neck injury, or the person develops any signs or symptoms of a serious head injury.
Prevention
Not all head injuries can be prevented. The following simple steps can help keep you and your child safe:
- Always use safety equipment during activities that could cause a head injury. These include seat belts, bicycle or motorcycle helmets, and hard hats.
- Learn and follow bicycle safety recommendations.
- Do not drink and drive, and do not allow yourself to be driven by someone who you know or suspect has been drinking alcohol or is impaired in another way.
Related Information
Traumatic brain injuryConcussion in adults - what to ask your doctor
Concussion in children - what to ask your doctor
Concussion in children - discharge
Concussion in adults - discharge
Preventing head injuries in children
References
Hockenberry B, Pusateri M, McGrew C. Sports-related head injuries. In: Kellerman RD, Rakel DP, eds. Conn's Current Therapy 2023. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:810-814.
Hudgins E, Heman-Ackah SM, Grady MS. Initial resuscitation, prehospital care, and emergency department care in traumatic brain injury. In: Winn HR, ed. Youmans and Winn Neurological Surgery. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 386.
Papa L, Goldberg SA. Head trauma. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 33.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 11/2/2023
Reviewed By: Jesse Borke, MD, CPE, FAAEM, FACEP, Attending Physician at Kaiser Permanente, Orange County, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2025 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
