BAER - brainstem auditory evoked response
Evoked auditory potentials; Brainstem auditory evoked potentials; Evoked response audiometry; Auditory brainstem response; ABR; BAEP
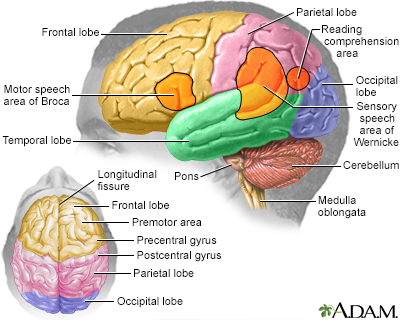
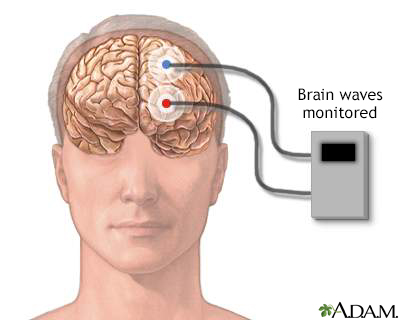
Brainstem auditory evoked response (BAER) is a test to measure the brain wave activity that occurs in response to clicks or certain tones.
Images
I Would Like to Learn About:
How the Test is Performed
You lie on a reclining chair or bed and remain still. Electrodes are placed on your scalp and on each earlobe. A brief click or tone will be transmitted through earphones you are wearing during the test. The electrodes pick up the brain's responses to these sounds and record them. You do not need to be awake for this test.
How to Prepare for the Test
You may be asked to wash your hair the night before the test.
Young children often need medicine to help them relax (sedation) so they can stay still during the procedure.
Why the Test is Performed
The test is done to:
- Help diagnose nervous system problems and hearing loss (especially in newborns and children)
- Find out how well the nervous system works
- Check hearing ability in people who cannot do other hearing tests
This test may also be performed during surgery to decrease the risk for injury to the hearing nerve and brain.
Normal Results
Normal results vary. Results will depend on the person and the instruments used to perform the test.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Abnormal test results may be a sign of hearing loss, multiple sclerosis, acoustic neuroma, or stroke.
Abnormal results may also be due to:
- Brain injury
- Brain malformation
- Brain tumor
- Central pontine myelinolysis
- Neurologic diseases
- Speech disorders
Risks
There are no risks associated with this test. There may be slight risks from having sedation depending on your age, medical conditions, and type of sedation medicine uses. Your provider will talk to you about any risk you may have.
Related Information
Hearing lossMultiple sclerosis
Stroke
Acoustic neuroma
Osmotic demyelination syndrome
References
Hahn CD, Emerson RG. Electroencephalography and evoked potentials. In: Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, Newman NJ, eds. Bradley and Daroff's Neurology in Clinical Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 35.
Kileny PR, Zwolan TA, Slager HK. Diagnostic audiology and electrophysiologic assessment of hearing. In: Flint PW, Francis HW, Haughey BH, et al, eds. Cummings Otolaryngology: Head and Neck Surgery. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 134.
Wackym PA. Neurotology. In: Winn HR, ed. Youmans and Winn Neurological Surgery. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 16.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 5/30/2022
Reviewed By: Josef Shargorodsky, MD, MPH, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2024 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
