Allergy testing - skin
Patch tests - allergy; Scratch tests - allergy; Skin tests - allergy; RAST test; Allergic rhinitis - allergy testing; Asthma - allergy testing; Eczema - allergy testing; Hayfever - allergy testing; Dermatitis - allergy testing; Allergy testing; Intradermal allergy testing
Allergy skin tests are used to find out which substances cause a person to have an allergic reaction. These substances are called allergens.
Images
How the Test is Performed
There are three common methods of allergy skin testing.
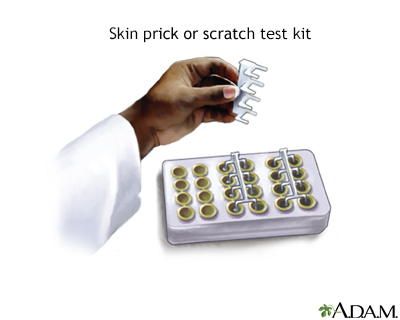
The skin prick test involves:
- Placing a small amount of substances (allergens) that may be causing your symptoms on the skin, most often on the forearm, upper arm, or back.
- The skin is then pricked so the allergen goes under the skin's surface.
- The health care provider closely watches the skin for swelling and redness or other signs of a reaction. Results are usually seen within 15 to 20 minutes.
- Several allergens can be tested at the same time.
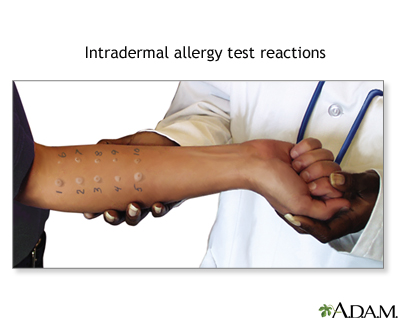
The intradermal skin test involves:
- Injecting a small amount of allergen into the skin.
- The provider then watches for a reaction at the site.
- This test is more likely to be used to find out if you're allergic to bee venom or penicillin. Or it may be used if the skin prick test was negative and the provider still thinks that you're allergic to the allergen.
Patch testing is a method to diagnose the cause of skin reactions that occur after the substance touches the skin:
- Possible allergens are taped to the skin for 48 hours.
- The provider will look at the area in 72 to 96 hours.
How to Prepare for the Test
Before any allergy testing, the provider will ask about:
- Illnesses
- Where you live and work
- Lifestyle
- Foods and eating habits
Allergy medicines can change the results of skin tests. Your provider will tell you which medicines to avoid and when to stop taking them before the test.
How the Test will Feel
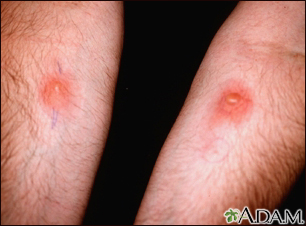
Skin tests may cause very mild discomfort when the skin is pricked. Positive skin tests will become red, itchy and swollen like a bug bite.
You may have symptoms such as itching, a stuffy nose, red watery eyes, or a skin rash if you're allergic to the substance in the test.
In rare cases, people can have a whole-body allergic reaction (called anaphylaxis), which can be life threatening. This usually only occurs with intradermal testing. Your provider will be prepared to treat this serious response.
Patch tests may be irritating or itchy. These symptoms will go away when the patch tests are removed.
Why the Test is Performed
Allergy tests are done to find out which substances are causing your allergy symptoms.
Your provider may order allergy skin tests if you have:
- Hay fever (allergic rhinitis) and asthma symptoms that are not well controlled with medicine
- Hives and angioedema
- Food allergies
- Skin rashes (dermatitis), in which the skin becomes red, sore, or swollen after contact with the substance
- Penicillin allergy
- Venom allergy
Allergies to penicillin and related medicines are the only medicine allergies that can be tested using skin tests.
The skin prick test may also be used to diagnose food allergies. Intradermal tests are not used to test for food allergies because of high false-positive results and the danger of causing a severe allergic reaction.
Normal Results
A negative test result means there were no skin changes in response to the allergen. This negative reaction most often means that you are not allergic to the substance.
In rare cases, a person may have a negative allergy test and still be allergic to the substance.
What Abnormal Results Mean
A positive result means you reacted to a substance. Your provider will see a red, raised area called a wheal.
Often, a positive result means the symptoms you're having are due to exposure to that substance. A stronger response means you are likely more sensitive to the substance.
People can have a positive response to a substance with allergy skin testing, but not have any problems with that substance in everyday life. Food allergy testing particularly carries a high risk of these false positive results.
Skin tests are usually accurate. But, if the dose of allergen is large, even people who are not allergic will have a positive reaction.
Your provider will consider your symptoms and the results of your skin test to suggest lifestyle changes you can make to avoid substances that may be causing your symptoms.
Related Information
AllergiesAllergen
Allergic rhinitis
Angioedema
Contact dermatitis
Stuffy or runny nose – adult
Allergic rhinitis - what to ask your doctor - adult
Allergic rhinitis - what to ask your doctor - child
References
Chiriac AM, Bousquet J, Demoly P. In vivo methods for the study and diagnosis of allergy. In: Burks AW, Holgate ST, O'Hehir RE, et al, eds. Middleton's Allergy: Principles and Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 67.
Homburger HA, Hamilton RG. Allergic diseases. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 56.
Nadeau KC. Approach to the patient with allergic or immunologic disease. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 230.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 3/31/2024
Reviewed By: Deborah Pedersen, MD, MS, Allergy & Asthma Care, PC, Taunton, MA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2025 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
