Chloride test - blood
Serum chloride test
Chloride is a type of electrolyte. It works with other electrolytes such as potassium, sodium, and carbon dioxide (CO2). These substances help keep the proper balance of body fluids and maintain the body's acid-base balance.
This article is about the laboratory test used to measure the amount of chloride in the fluid portion (serum) of the blood.
Images
I Would Like to Learn About:
How the Test is Performed
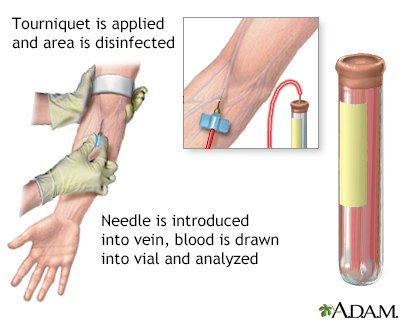
A blood sample is needed. Most of the time blood is drawn from a vein located on the inside of the elbow or the back of the hand.
How to Prepare for the Test
Many medicines can interfere with blood test results.
- Your health care provider will tell you if you need to stop taking any medicines before you have this test.
- DO NOT stop or change your medicines without talking to your provider first.
Why the Test is Performed
You may have this test if you have signs that your body's fluid level or acid-base balance is disturbed.
This test is most often ordered with other blood tests, such as a basic or comprehensive metabolic panel.
Normal Results
A typical normal range is 96 to 106 milliequivalents per liter (mEq/L) or 96 to 106 millimoles per liter (millimol/L).
Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Talk to your provider about the meaning of your specific test results.
The example above shows the common measurement range for results for these tests. Some laboratories use different measurements or may test different specimens.
What Abnormal Results Mean
A greater-than-normal level of chloride is called hyperchloremia. It may be due to:
- Addison disease
- Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (used to treat glaucoma)
- Diarrhea
- Ethylene glycol poisoning
- Ketoacidosis
- Kidney disease
- Lactic acidosis
- Metabolic acidosis
- Methanol poisoning
- Renal tubular acidosis - distal
- Renal tubular acidosis - proximal
- Respiratory alkalosis (compensated)
- Salicylate toxicity (such as aspirin overdose)
- Ureteral diversion
A lower-than-normal level of chloride is called hypochloremia. It may be due to:
- Bartter syndrome
- Burns
- Congestive heart failure
- Cushing syndrome
- Dehydration
- Excessive sweating
- Hyperaldosteronism
- Metabolic alkalosis
- Respiratory acidosis (compensated)
- Syndrome of inappropriate diuretic hormone secretion (SIADH)
- Vomiting
This test may also be done to help rule out or diagnose:
- Multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) II
- Primary hyperparathyroidism
Delirium may also alter chloride levels.
Related Information
IonsSodium blood test
Hyperventilation
Metabolic acidosis
Proximal renal tubular acidosis
Addison disease
Respiratory acidosis
Heart failure
Gastric suction
Antidiuretic hormone blood test
Multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) II
References
Bansal A. Respiratory acidosis, respiratory alkalosis, and mixed acid-base disorders. In: Johnson RJ, Floege J, Tonelli M, eds. Comprehensive Clinical Nephrology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 15.
Seifter JR. Acid-base disorders. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 110.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 6/20/2023
Reviewed By: Jacob Berman, MD, MPH, Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine, Division of General Internal Medicine, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2025 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
