Alanine transaminase (ALT) blood test
SGPT; Serum glutamate pyruvate transaminase; Alanine transaminase; Alanine aminotransferase
The alanine transaminase (ALT) blood test measures the level of the enzyme ALT in the blood.
Images
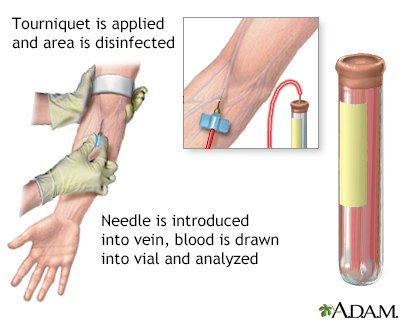
How the Test is Performed
A blood sample is needed.
How to Prepare for the Test
No special preparation is needed.
How the Test will Feel
When the needle is inserted to draw blood, some people feel moderate pain. Others feel only a prick or stinging. Afterward, there may be some throbbing or a slight bruise. This soon goes away.
Why the Test is Performed
ALT is an enzyme found in a high level in the liver. An enzyme is a protein that causes a specific chemical change in the body.
Injury to the liver results in release of ALT into the blood.
This test is mainly done along with other tests (such as AST, ALP, and bilirubin) to diagnose and monitor liver disease.
Normal Results
The normal range is 4 to 36 U/L (0.07 to 0.60 µkat/L).
Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different labs. Some labs use different measurements or may test different samples. Talk to your health care provider about the meaning of your specific test results.
What Abnormal Results Mean
An increased ALT level is often a sign of liver disease. Liver disease is even more likely when the levels of substances checked by other liver blood tests have also increased.
An increased ALT level may be due to any of the following:
- Scarring of the liver (cirrhosis)
- Death of liver tissue
- Swollen and inflamed liver (hepatitis)
- Too much iron in the body (hemochromatosis)
- Too much fat in the liver (fatty liver)
- Lack of blood flow to the liver (liver ischemia)
- Liver tumor or cancer
- Use of medicines and drugs that are toxic to the liver (such as alcohol or acetaminophen)
- Mononucleosis ("mono")
- Swollen and inflamed pancreas (pancreatitis)
Risks
There is little risk involved with having your blood taken. Veins and arteries vary in size from one person to another and from one side of the body to the other. Taking blood from some people may be more difficult than from others.
Other risks associated with having blood drawn are slight, but may include:
- Excessive bleeding
- Fainting or feeling lightheaded
- Multiple punctures to locate veins
- Hematoma (blood collecting under the skin)
- Infection (a slight risk any time the skin is broken)
Related Information
EnzymeMetabolism
Hepatitis
Hepatic
Cirrhosis
Liver cancer - hepatocellular carcinoma
References
Daniels L, Khalili M, Goldstein E, Bluth MH, Bowne WB, Pincus MR. Evaluation of liver function. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 22.
Pratt DS. Liver chemistry and function tests. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 73.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 1/1/2025
Reviewed By: Frank D. Brodkey, MD, FCCM, Associate Professor, Section of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health, Madison, WI. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2025 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
