X-ray - skeleton
Skeletal survey
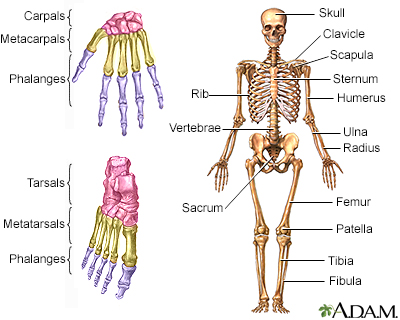
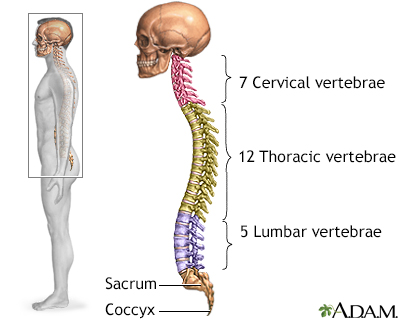
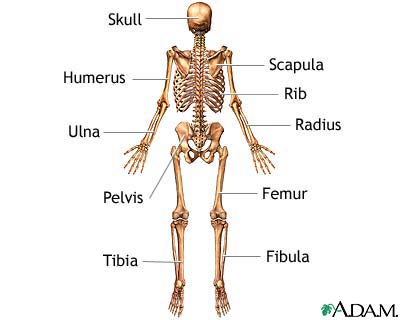
A skeletal x-ray is an imaging test used to look at your bones. It is used to detect fractures, tumors, or conditions that cause wearing away (degeneration) of the bone.
Images

I Would Like to Learn About:
How the Test is Performed
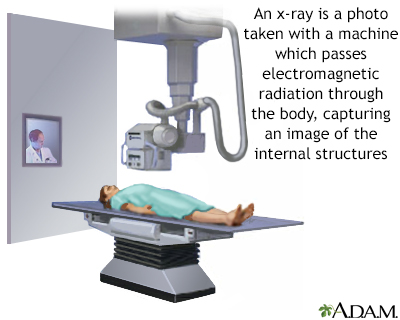
The test is done in a hospital radiology department or in your health care provider's office by an x-ray technologist.
You will lie on a table or stand in front of the x-ray machine, depending on the bone that is injured. You may be asked to change position so that different x-ray views can be taken.
The x-rays pass through your body. A computer or special film records the images.
Structures that are dense (such as bone) will block most of the x-ray particles. These areas will appear white. Metal and contrast media (special dye used to highlight areas of the body) will also appear white. Structures containing air will be black. Muscle, fat, and fluid will appear as shades of gray.
How to Prepare for the Test
Tell your provider if you are pregnant. You must remove all jewelry before the x-ray.
How the Test will Feel
The x-rays are painless. Changing positions and moving the injured area for different x-ray views may be uncomfortable. If the whole skeleton is being imaged, the test most often takes 1 hour or more.
Why the Test is Performed
This test is used to look for:
- Fractures or broken bone
- Cancer that has spread to other areas of the body
- Osteomyelitis (inflammation of the bone caused by an infection)
- Bone damage due to trauma (such as an auto accident) or degenerative conditions
- Abnormalities in the soft tissue around the bone
What Abnormal Results Mean
Abnormal findings include:
- Fractures
- Bone tumors
- Degenerative bone conditions
- Osteomyelitis
Risks
There is low radiation exposure. X-rays machines are set to provide the smallest amount of radiation exposure needed to produce the image. Most experts feel that the risk is low compared with the benefits.
Children and the fetuses of pregnant women are more sensitive to the risks of the x-ray. A protective shield may be worn over areas not being scanned.
Related Information
X-rayBroken bone
Metastasis
Cancer
Osteomyelitis
Bone tumor
References
Contreras F, Perez J, Jose J. Imaging overview. In: Miller MD, Thompson SR, eds. DeLee, Drez, & Miller's Orthopaedic Sports Medicine. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 7.
Kapoor G, Toms AP. Current status of imaging of the musculoskeletal system. In: Adam A, Dixon AK, Gillard JH, Schaefer-Prokop CM, eds. Grainger & Allison's Diagnostic Radiology: A Textbook of Medical Imaging. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 38.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 4/27/2023
Reviewed By: Linda J. Vorvick, MD, Clinical Professor, Department of Family Medicine, UW Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2024 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
