Sensorineural deafness
Nerve deafness; Hearing loss - sensorineural; Acquired hearing loss; SNHL; Noise-induced hearing loss; NIHL; Presbycusis
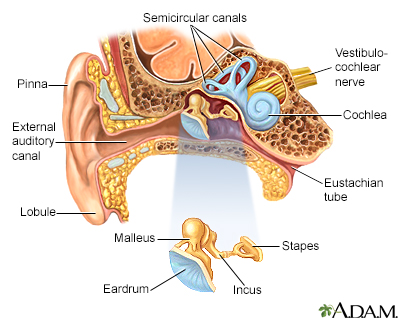
Sensorineural deafness is a type of hearing loss. It occurs from damage to the inner ear, the place of origin of the nerve that runs from the ear to the brain (auditory nerve), or damage to the brain itself.
Images
I Would Like to Learn About:
Considerations
Symptoms may include:
- Some sounds seem overly loud in one ear.
- You have problems following conversations when two or more people are talking.
- You have problems hearing in noisy areas.
- It is easier to hear men's voices than women's voices.
- It is hard to tell high-pitched sounds (such as "s" or "th") from one another.
- Other people's voices sound mumbled or slurred.
- You have problems hearing when there is background noise.
Associated symptoms may include:
- Feeling of being off-balance or dizzy (more common with Meniere disease and acoustic neuromas)
- Ringing or buzzing sound in the ears (tinnitus)
Causes
The inner part of the ear contains tiny hair cells (nerve endings), that change sounds into electric signals. The nerves then carry these signals to the brain.
Sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) is caused by damage to these special cells, or to the nerve fibers in the inner ear. Sometimes, the hearing loss is caused by damage to the nerve that carries the signals to the brain.
Sensorineural deafness that is present at birth (congenital) is most often due to:
- Genetic syndromes
- Infections that the mother passes to her baby in the womb (toxoplasmosis, rubella, herpes)
SNHL may develop in children or adults later in life (acquired) as a result of:
- Age-related hearing loss
- Disease of the blood vessels
- Immune disease
- Infections, such as meningitis, mumps, scarlet fever, and measles
- Injury of the ear or head
- Loud noises or sounds, or loud sounds that last for a long time
- Meniere disease
- Tumor, such as acoustic neuroma
- Use of certain medicines
- Working around loud noises every day
In some cases, the cause is unknown.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
The goal of treatment is to improve your hearing. The following may be helpful:
- Hearing aids
- Telephone amplifiers and other assistive devices
- Safety and alert systems for your home
- Sign language (for those with severe hearing loss)
- Speech reading (such as lip reading and using visual cues to aid communication)
A cochlear implant may be recommended for certain people with severe hearing loss. Surgery is done to place the implant. The implant makes sounds seem louder, but does not restore normal hearing.
You will also learn strategies for living with hearing loss and advice to share with those around you for talking to someone with hearing loss.
Related Information
Hearing lossReferences
Arts HA, Adams ME. Sensorineural hearing loss in adults. In: Flint PW, Francis HW, Haughey BH, et al, eds. Cummings Otolaryngology: Head and Neck Surgery. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 152.
Eggermont JJ. Types of hearing loss. In: Eggermont JJ, ed. Hearing Loss. Cambridge, MA: Elsevier Academic Press; 2017:chap 5.
Le Prell CG. Noise-induced hearing loss. In: Flint PW, Francis HW, Haughey BH, et al, eds. Cummings Otolaryngology: Head and Neck Surgery. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 154.
National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders website. Noise-induced hearing loss. NIH Pub. No. 14-4233. www.nidcd.nih.gov/health/noise-induced-hearing-loss. Updated March 16, 2022. Accessed May 8, 2024.
Shearer AE, Shibata SB, Smith RJH. Genetic sensorineural hearing loss. In: Flint PW, Francis HW, Haughey BH, et al, eds. Cummings Otolaryngology: Head and Neck Surgery. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 150.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 5/2/2024
Reviewed By: Josef Shargorodsky, MD, MPH, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2025 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
