Diarrhea
Stools - watery; Frequent bowel movements; Loose bowel movements; Unformed bowel movements
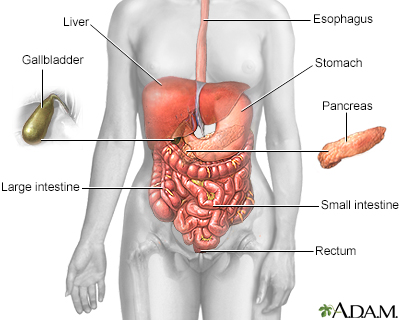
Diarrhea is when you pass loose or watery stool.
Images
Considerations
In some people, diarrhea is mild and goes away in a few days. In other people, it may last longer.
Diarrhea can make you feel weak and dehydrated.
Diarrhea in babies and children can be serious. It needs to be treated differently than you would treat diarrhea in adults.
Talk with your health care provider if your child has diarrhea. There can be a lot to know. Your provider can help you learn how to recognize and treat diarrhea in babies and in children.
Causes
The most common cause of diarrhea is the stomach flu (viral gastroenteritis). This mild viral infection most often goes away on its own within a few days.
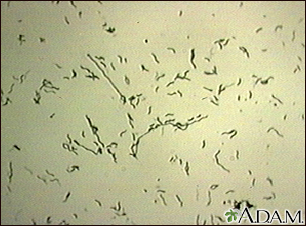
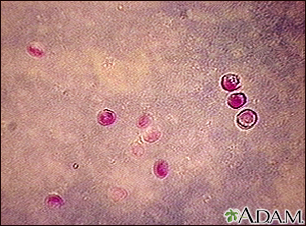
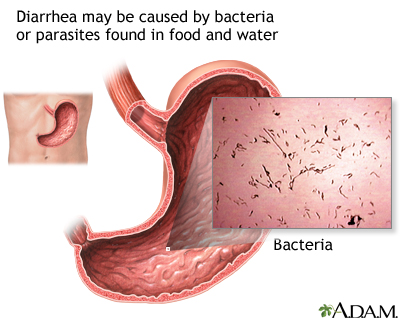
Eating or drinking food or water that contains certain types of bacteria or parasites can also lead to diarrhea. This problem may be called food poisoning.
Certain medicines may also cause diarrhea, including:
- Some antibiotics
- Chemotherapy drugs for cancer
- Laxatives containing magnesium
Diarrhea may also be caused by medical disorders, such as:
- Celiac disease
- Inflammatory bowel diseases (Crohn disease and ulcerative colitis)
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
- Lactose intolerance (which causes problems after drinking milk and eating other dairy products)
- Malabsorption syndromes
Less common causes of diarrhea include:
- Carcinoid syndrome
- Disorders of the nerves that supply the intestines
- Removal of part of the stomach (gastrectomy) or small intestine
- Radiation therapy
People who travel to developing countries can get diarrhea from unclean water or food that has not been handled safely. Plan ahead by learning the risks and treatment for traveler's diarrhea before your trip.
Home Care
Most times, you can treat diarrhea at home. You will need to learn:
- To drink plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration (when your body does not have the proper amount of water and fluids)
- Which foods you should or should not eat
- What to do if you are breastfeeding
- What danger signs to watch for
Avoid medicines for diarrhea that you can buy without a prescription unless your provider tells you to use them. These drugs can make some infections worse.
If you have a long-term form of diarrhea, such as diarrhea caused by irritable bowel syndrome, changes to your diet and lifestyle may help.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider right away if you or your child shows signs of dehydration:
- Decreased urine (fewer wet diapers in infants)
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Dry mouth
- Sunken eyes
- Few tears when crying
Schedule an appointment with your provider if you have:
- Blood or pus in your stools
- Black stools
- Stomach pain that does not go away after a bowel movement
- Diarrhea with a fever above 101°F or 38.33°C (100.4°F or 38°C in children)
- Recently traveled to a foreign country and developed diarrhea
Also contact your provider if:
- The diarrhea gets worse or does not get better in 2 days for an infant or child, or 5 days for adults
- A child over 3 months old has been vomiting for more than 12 hours; in younger babies, call as soon as vomiting or diarrhea begins
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your provider will perform a physical exam and ask about your medical history and symptoms.
Lab tests may be done on your stools to find the cause of your diarrhea.
This is also a good time to ask your provider any questions you have about diarrhea.
Over-the-counter supplements that contain healthy bacteria may help prevent diarrhea caused by taking antibiotics. These are called probiotics. Yogurt with active or live cultures is also a good source of these healthy bacteria.
The following healthy steps can help you prevent illnesses that cause diarrhea:
- Wash your hands often, particularly after using the toilet and before eating.
- Use alcohol-based hand gel frequently.
- Teach children to not put objects in their mouth.
- Take steps to avoid food poisoning.
When traveling to underdeveloped areas, follow the steps below to avoid diarrhea:
- Drink only bottled water and DO NOT use ice, unless it is made from bottled or purified water.
- DO NOT eat uncooked vegetables or fruits that do not have peels.
- DO NOT eat raw shellfish or undercooked meat.
- DO NOT consume dairy products.
Related Information
Clear liquid dietFull liquid diet
Diarrhea - what to ask your health care provider - adult
Diarrhea - what to ask your doctor - child
When you have nausea and vomiting
References
Schiller LR, Sellin JH. Diarrhea. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 16.
Semrad CE. Approach to the patient with diarrhea and malabsorption. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 131.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 11/3/2022
Reviewed By: Michael M. Phillips, MD, Emeritus Professor of Medicine, The George Washington University School of Medicine, Washington, DC. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2025 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
