Dizziness
Lightheadedness - dizzy; Loss of balance; Vertigo
Dizziness is a term that is often used to describe 2 different symptoms: lightheadedness and vertigo.
Lightheadedness is a feeling that you might faint.
Vertigo is a feeling that you are spinning or moving, or that the world is spinning around you. Vertigo-associated disorders is a related topic.
Images
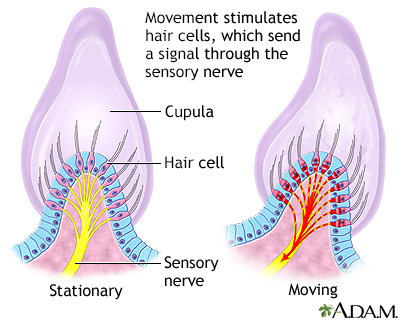
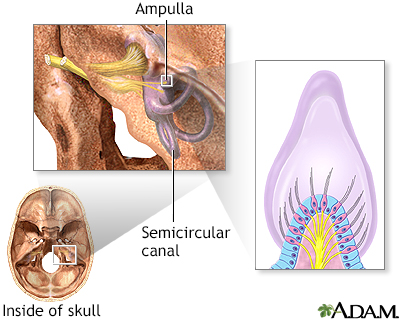
I Would Like to Learn About:
Considerations
Most causes of dizziness are not serious, and they either quickly get better on their own or are easy to treat.
Causes
Lightheadedness occurs when your brain does not get enough blood. This may occur if:
- You have a sudden drop in blood pressure.
- Your body does not have enough water (is dehydrated) because of vomiting, diarrhea, fever, or other conditions.
- You get up too quickly after sitting or lying down (this is more common in older people).
Lightheadedness may also occur if you have the flu, low blood sugar, a cold, allergies, or take medicines that may lower your blood pressure.
More serious conditions that can lead to lightheadedness include:
- Heart problems, such as a heart attack or abnormal heart beat
- Stroke
- Bleeding inside the body
- Shock (extreme drop in blood pressure)
If any of these serious disorders are present, you will usually also have symptoms like chest pain, a feeling of a racing heart, loss of speech, change in vision, or other symptoms.
Vertigo may be due to:
- Benign positional vertigo, a spinning feeling that occurs when you move your head
- Labyrinthitis, a viral infection of the inner ear that usually follows a cold or flu
- Meniere disease, a common inner ear problem
Other causes of lightheadedness or vertigo may include:
- Use of certain medicines
- Stroke
- Multiple sclerosis
- Seizures
- Brain tumor
- Bleeding in the brain
Home Care
If you tend to get lightheaded when you stand up:
- Avoid sudden changes in posture.
- Get up from a lying position slowly, and stay seated for a few moments before standing.
- When standing, make sure you have something to hold on to.
If you have vertigo, the following tips can help prevent your symptoms from becoming worse:
- Keep still and rest when symptoms occur.
- Avoid sudden movements or position changes.
- Slowly increase activity.
- You may need a cane or other help walking when you have a loss of balance during a vertigo attack.
- Avoid bright lights, TV, and reading during vertigo attacks because they may make symptoms worse.
Avoid activities such as driving, operating heavy machinery, and climbing until 1 week after your symptoms disappear. A sudden dizzy spell during these activities can be dangerous.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your local emergency number (such as 911) or go to an emergency room if you are dizzy and have:
- A head injury
- Fever over 101°F (38.3°C), headache, or very stiff neck
- Seizures
- Trouble keeping fluids down
- Chest pain
- Irregular heart rate (heart is skipping beats)
- Shortness of breath
- Weakness
- Inability to move an arm or leg
- Change in vision or speech
- Fainting and loss of alertness for more than a few minutes
Contact your health care provider for an appointment if you have:
- Dizziness for the first time
- New or worsening symptoms
- Dizziness after taking medicine
- Hearing loss
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your provider will perform a physical exam and ask questions about your medical history and symptoms, including:
- When did your dizziness begin?
- Does your dizziness occur or get worse when you move?
- What other symptoms occur when you feel dizzy?
- Are you always dizzy or does the dizziness come and go?
- How long does the dizziness last?
- Were you sick with a cold, flu, or other illness before the dizziness began?
- Do you have a lot of stress or anxiety?
Tests that may be done include:
- Blood pressure reading
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Hearing tests
- Balance testing (ENG)
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Your provider may prescribe medicines to help you feel better, including:
- Antihistamines
- Sedatives
- Anti-nausea medicine
Surgery may be needed if you have Meniere disease.
References
Baloh RW, Jen JC. Hearing and equilibrium. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 428.
Chang AK. Dizziness and vertigo. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 15.
Muncie HL, Sirmans SM, James E. Dizziness: approach to evaluation and management. Am Fam Physician. 2017;95(3):154-162. PMID: 28145669 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28145669/.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 4/27/2023
Reviewed By: Linda J. Vorvick, MD, Clinical Professor, Department of Family Medicine, UW Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2025 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
