Wheezing
Sibilant rhonchi; Wheezing asthma; Wheezing - bronchiectasis; Wheezing - bronchiolitis; Wheezing - bronchitis; Wheezing - COPD; Wheezing - heart failure
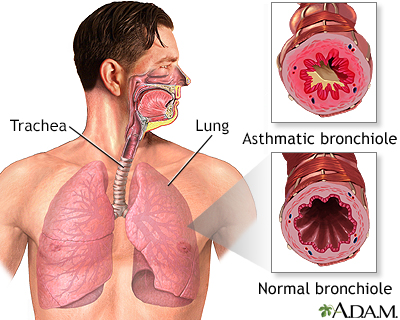
Wheezing is a high-pitched whistling sound during breathing. It occurs when air moves through narrowed breathing tubes in the lungs.
Images
Considerations
Wheezing is a sign that a person may be having breathing problems. The sound of wheezing is most apparent when breathing out (exhaling). It may also be heard when breathing in (inhaling).
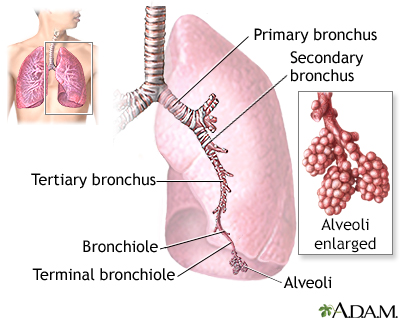
Wheezing most often comes from the small breathing tubes (bronchial tubes) deep in the lungs. But it may be due to a blockage in larger airways or in people with certain vocal cord problems.
Causes
Causes of wheezing may include any of the following:
- Asthma
- Breathing a foreign object into the airways to the lungs
- Damage and widening of the large airways in the lungs (bronchiectasis)
- Swelling and mucus buildup in the smallest air passages in the lungs (bronchiolitis)
- Swelling and mucus buildup in the main passages that carry air to the lungs (bronchitis)
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), especially when a respiratory infection is present
- Acid reflux disease
- Heart failure (cardiac asthma)
- Insect sting that causes an allergic reaction
- Certain medicines (such as aspirin)
- Infection of the lungs (pneumonia)
- Smoking
- Viral infection, especially in infants younger than age 2
Home Care
Take all of your medicines as directed.
Sitting in an area where there is moist, heated air may help relieve some symptoms. This can be done by running a hot shower or using a vaporizer.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider if wheezing:
- Occurs for the first time
- Occurs with significant shortness of breath, bluish skin, confusion, or mental status changes
- Keeps occurring without explanation
- Is caused by an allergic reaction to a bite or medicine
If wheezing is severe or occurs with severe shortness of breath, you should go directly to the nearest emergency department.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your provider will perform a physical exam and ask about your medical history and symptoms. Questions about your wheezing may include when it started, how long it has lasted, when it is worse, and what might have caused it.
The physical exam may include listening to the lung sounds (auscultation). If your child has the symptoms, their provider will make sure your child didn't swallow a foreign object.
Tests that may be done include:
- Blood tests, possibly including arterial blood gases
- Chest x-ray
- Lung function tests
- Pulse oximetry to measure blood oxygen level
A hospital stay may be needed if:
- Breathing is particularly difficult
- Medicines need to be given through a vein (IV)
- Supplemental oxygen is required
- The person needs to be closely watched by medical personnel
Related Information
Asthma - control drugsHow to use a nebulizer
Asthma - quick-relief drugs
Asthma and school
Exercise-induced asthma
References
Doss AMA, Stokes JR. Viral infections and wheezing in preschool children. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2022;42(4):727-741. PMID: 36265972 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36265972/.
Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al. Wheezing, bronchiolitis, and bronchitis. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 439.
Woodruff PG, Bhakta NR, Ortega VE, Lambrecht BN, Fahy JV. Asthma: pathogenesis and phenotypes. In: Broaddus VC, Ernst JD, King TE, et al, eds. Murray and Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 60.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 4/1/2024
Reviewed By: Charles I. Schwartz, MD, FAAP, Clinical Assistant Professor of Pediatrics, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, General Pediatrician at PennCare for Kids, Phoenixville, PA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2025 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
