Ear discharge
Drainage from the ear; Otorrhea; Ear bleeding; Bleeding from ear
Ear discharge is drainage of blood, ear wax, pus, or fluid from the ear.
Images
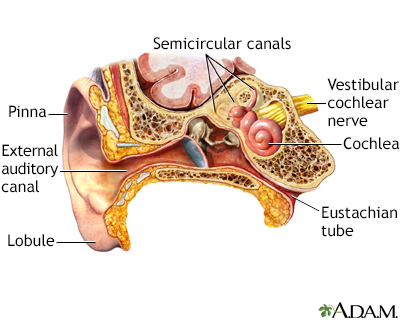
Presentation

I Would Like to Learn About:
Causes
Most of the time, any fluid leaking out of an ear is ear wax.
A ruptured eardrum can cause a white, slightly bloody, or yellow discharge from the ear. Dry crusted material on a child's pillow is often a sign of a ruptured eardrum. The eardrum may also bleed.
Causes of a ruptured eardrum include:
- Foreign object in the ear canal
- Injury from a blow to the head, foreign object, very loud noises, or sudden pressure changes (such as in airplanes)
- Inserting cotton-tipped swabs or other small objects into the ear
- Middle ear infection
Other causes of ear discharge include:
- Eczema and other skin irritations in the ear canal
- Swimmer's ear with symptoms such as itching, scaling, a red or moist ear canal, and pain that increases when you move the earlobe
- Normal ear wax
Home Care
Caring for ear discharge at home depends on the cause.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider if:
- The discharge is white, yellow, clear, or bloody.
- The discharge is the result of an injury.
- The discharge has lasted more than 5 days.
- There is severe pain.
- The discharge is associated with other symptoms, such as fever or headache.
- There is loss of hearing.
- There is redness or swelling coming out of the ear canal.
- Facial weakness or asymmetry
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
The provider will perform a physical exam and look inside the ears. You may be asked questions, such as:
- When did the ear drainage begin?
- What does it look like?
- How long has it lasted?
- Does it drain all the time or off-and-on?
- What other symptoms do you have (for example, fever, ear pain, headache, or hearing loss)?
The provider may take a sample of the ear drainage and send it to a lab for examination.
The provider may recommend anti-inflammatory or antibiotic medicines, which are liquid drops placed in the ear. Antibiotics may be given by mouth if a ruptured eardrum from an ear infection is causing the discharge.
The provider may remove wax or infectious material from the ear canal using a small vacuum suction.
Related Information
Ear waxRuptured eardrum
Earache
Ear tube surgery - what to ask your doctor
References
Hathorn I. The ear, nose and throat. In: Innes JA, Dover AR, Fairhurst K, eds. Macleod's Clinical Examination. 15th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 9.
Pelton SI. Otitis externa, otitis media, and mastoiditis. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 61.
Player B. Otitis media. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 680.
Wareing MJ, Warner E. Ear, nose and throat. In: Glynn M, Drake WM, eds. Hutchison's Clinical Methods. 25th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 22.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 5/2/2024
Reviewed By: Josef Shargorodsky, MD, MPH, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2025 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
