Oral mucous cyst
Mucocele; Mucous retention cyst; Ranula
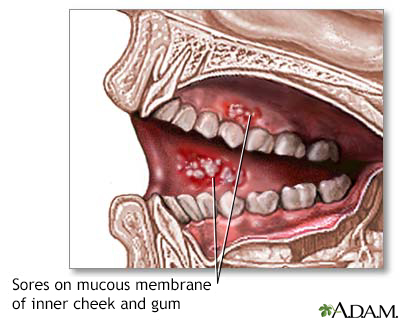
An oral mucous cyst is a painless, thin sac on the inner surface of the mouth. It contains clear fluid.
Images
I Would Like to Learn About:
Causes
Mucous cysts most often appear near salivary gland openings (ducts). Common sites and causes of cysts include:
- Inner surface of the upper or lower lip, inside the cheeks, bottom surface of the tongue. These are called mucoceles. They are often caused by lip biting, lip sucking, or other trauma.
- Floor of the mouth. These are called ranula. They are caused by blockage of the salivary glands under the tongue.
Symptoms
Symptoms of mucoceles include:
- Usually painless, but can be bothersome because you're aware of the bumps in your mouth.
- Often appears clear, bluish or pink, soft, smooth, round and dome-shaped.
- Vary in size up to 1 cm in diameter.
- May break open on their own, but may recur.
Symptoms of ranula include:
- Usually painless swelling on the floor of the mouth below the tongue.
- Often appears bluish and dome-shaped.
- If the cyst is large, chewing, swallowing, talking may be affected.
- If the cyst grows into the neck muscle, breathing can stop. This is a medical emergency.
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider can usually diagnose a mucocele or ranula simply by looking at it. Other tests that may be done include:
- Biopsy
- Ultrasound
- CT scan, usually for ranula that has grown into the neck
Treatment
A mucous cyst often can be left alone. It usually will rupture on its own. If the cyst returns, it may need to be removed.
To remove a mucocele, the provider may perform any of the following:
- Freezing the cyst (cryotherapy)
- Laser treatment
- Surgery to cut out the cyst
A ranula is usually removed using laser or surgery. The best outcome is removing both the cyst and the gland that caused the cyst.
To prevent infection and damage to the tissue, do not try to open the sac yourself. Treatment should only be done by your provider. Oral surgeons and some dentists can remove the sac.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- Return of the cyst
- Injury of nearby tissues during removal of a cyst
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you:
- Notice a cyst or mass in your mouth
- Have difficulty swallowing or talking
These may be a sign of more serious problem, such as mouth cancer.
Prevention
Avoiding intentionally sucking the cheeks or biting the lips may help prevent some mucoceles.
Related Information
CystVesicles
References
Kim WE. Disorders of the mucous membranes. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 684.
Patterson JW. Cysts, sinuses, and pits. In: Patterson JW, ed. Weedon's Skin Pathology. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 17.
Woo BM. Sublingual gland excision and ductal surgery. In: Kademani D, Tiwana PS, eds. Atlas of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. St Louis, MO: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 86.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 7/25/2022
Reviewed By: Linda J. Vorvick, MD, Clinical Professor, Department of Family Medicine, UW Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2024 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
