Bartholin cyst or abscess
Abscess - Bartholin; Infected Bartholin gland; Bartholin's cyst or abscess
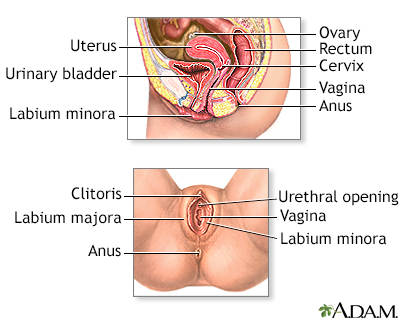
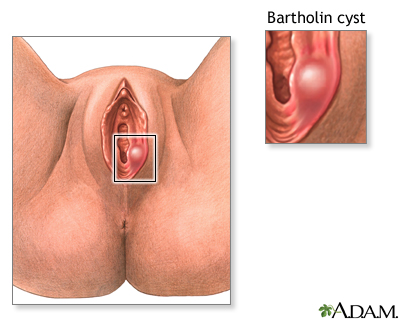
Bartholin abscess is the buildup of pus that forms a lump (swelling) in one of the Bartholin glands. These glands are found on each side of the vaginal opening.
Images
Causes
A Bartholin abscess forms when a small opening (duct) from the gland gets blocked. Fluid in the gland builds up and may become infected. Fluid may build up over many years before an abscess occurs.
Often the abscess appears quickly over several days. The area will become very warm and swollen. Activity that puts pressure on the vulva, and walking and sitting, may cause severe pain.
Symptoms
Symptoms may include:
- A tender lump on either side of the vaginal opening
- Swelling and redness
- Pain with sitting or walking
- Fever, in people with low immunity
- Pain with sexual intercourse
- Vaginal discharge
- Vaginal pressure
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will do a pelvic exam. The Bartholin gland will be enlarged and tender. In rare cases, a biopsy may be suggested in older women to look for a tumor.
Any vaginal discharge or fluid drainage will be sent to a lab for testing.
Treatment
SELF-CARE STEPS
Soaking in warm water 4 times a day for several days can ease the discomfort. It can also help the abscess open and drain on its own. However, the opening is often very small and closes quickly. Therefore, the abscess often returns.
DRAINAGE OF THE ABSCESS
A small surgical cut can completely drain the abscess. This relieves symptoms and provides the fastest recovery.
- The procedure can be done under local anesthesia in a provider's office.
- A 1 to 2 cm cut is made at the site of abscess. The cavity is irrigated with normal saline. A catheter (tube) may be inserted and left in place for 4 to 6 weeks. This allows continuous drainage while the area heals. Sutures are not required.
- You should begin soaking in warm water 1 to 2 days afterward. You cannot have sexual intercourse until the catheter is removed.
You may be asked to take antibiotics if there is pus or other signs of infection.
MARSUPIALIZATION
Women can also be treated with a minor surgery called marsupialization.
- The procedure involves creating an elliptical opening along the cyst to help the gland drain. The abscess is removed. The provider places stitches at the edges of the cyst.
- The procedure can sometimes be done in the clinic with medicine to numb the area. In other cases, it may need to be done in the hospital with general anesthesia so that you are asleep and pain-free.
- You should begin soaking in warm water 1 to 2 days afterward. You cannot have sexual intercourse for 4 weeks after surgery.
- You can use oral pain medicines after the procedure. Your provider may prescribe narcotic pain medicines if you need them.
EXCISION
Your provider may recommend that the glands be completely removed if abscesses keep coming back.
- The procedure involves surgical removal of the entire cyst wall.
- Generally performed in the hospital under general anesthesia.
- You cannot have sexual intercourse for 4 weeks after surgery.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The chance of a full recovery is excellent. The abscesses may return in a few cases.
It is important to treat any vaginal infection that is diagnosed at the same time as the abscess.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if:
- You notice a painful, swollen lump on the labia near the vagina opening and it does not improve with 2 to 3 days of home treatment.
- Pain is severe and interferes with your normal activity.
- You have one of these cysts and develop a fever higher than 100.4°F (38°C).
Related Information
SwellingAbscess
Vulva
References
Ambrose G, Berlin D. Incision and drainage. In: Roberts JR, Custalow CB, Thomsen TW, eds. Roberts and Hedges' Clinical Procedures in Emergency Medicine and Acute Care. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 37.
Dolan MS, Hill C, Valea FA. Benign gynecologic lesions: vulva, vagina, cervix, uterus, oviduct, ovary, ultrasound imaging of pelvic structures. In: Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA, Lobo RA, eds. Comprehensive Gynecology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 18.
Smith RP. Bartholin gland cyst/abscess drainage. In: Smith RP, ed. Netter's Obstetrics and Gynecology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 262.
Tuggy ML. Bartholin cyst and abscess: word catheter insertion marsupialization. In: Fowler GC, ed. Pfenninger and Fowler's Procedures for Primary Care. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 118.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 4/16/2024
Reviewed By: John D. Jacobson, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Loma Linda University School of Medicine, Loma Linda, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2025 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
