Aspergillosis
Aspergillus infection
Aspergillosis is an infection or allergic response due to the aspergillus fungus.
Images
Causes
Aspergillosis is caused by a fungus called aspergillus. The fungus is often found growing on dead leaves, stored grain, compost piles, or in other decaying vegetation. It can also be found on marijuana leaves.
Although most people are often exposed to aspergillus, infections caused by the fungus rarely occur in people who have a healthy immune system.
There are several forms of aspergillosis:
- Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis is an allergic reaction to the fungus. This infection usually develops in people who already have lung problems such as asthma or cystic fibrosis.
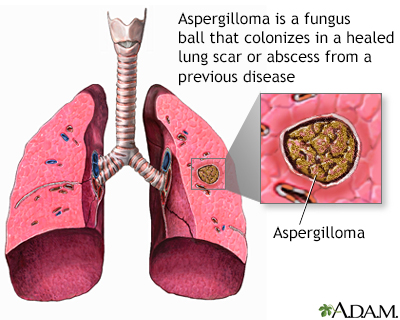
- Aspergilloma is a growth (fungus ball) that develops in an area of past lung disease or lung scarring such as tuberculosis or lung abscess.
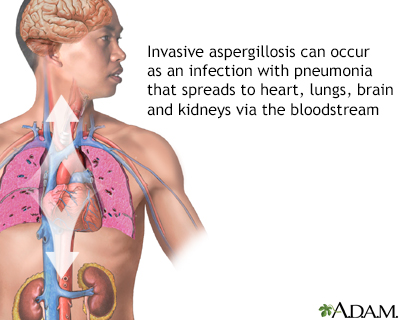
- Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis is a serious infection with pneumonia. It can spread to other parts of the body. This infection occurs most often in people with a weakened immune system. This can be from cancer, AIDS, leukemia, an organ transplant, chemotherapy, or other conditions or medicines that lower the number or function of white blood cells or weaken the immune system.
Symptoms
Symptoms depend on the type of infection.
Symptoms of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis may include:
- Cough
- Coughing up blood or brownish mucus plugs
- Fever
- General ill feeling (malaise)
- Wheezing
- Weight loss
Other symptoms depend on the part of the body affected, and may include:
- Bone pain
- Chest pain
- Chills
- Decreased urine output
- Headaches
- Increased phlegm production, which may be bloody
- Shortness of breath
- Skin sores (lesions)
- Vision problems
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will perform a physical examination and ask about the symptoms.
Tests to diagnose aspergillus infection include:
- Aspergillus antibody test
- Chest x-ray
- Complete blood count
- CT scan
- Galactomannan (a sugar molecule shed from the fungus that is sometimes found in the blood)
- Immunoglobulin E (IgE) blood level
- Lung function tests
- Sputum stain and culture for fungus (looking for aspergillus)
- Tissue biopsy
Treatment
A fungus ball is usually not treated with antifungal medicines unless there is bleeding into the lung tissue. In such a case, surgery and medicines are needed.
Invasive aspergillosis is treated with several weeks of an antifungal medicine. It can be given by mouth or IV (into a vein). Endocarditis caused by aspergillus is treated by surgically replacing the infected heart valves. Long-term antifungal medicines are also needed.
Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis is treated with medicines that suppress the immune system (immunosuppressive medicines), such as prednisone, typically in conjunction with antifungals.
Outlook (Prognosis)
With treatment, people with allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis usually get better over time. It is common for the disease to come back (relapse) and need repeat treatment.
If invasive aspergillosis does not get better with treatment using medicine, it eventually leads to death. The outlook for invasive aspergillosis also depends on the person's underlying disease and immune system health.
Possible Complications
Health problems from the disease or treatment include:
- Amphotericin B can cause kidney damage and unpleasant side effects such as fever and chills
- Bronchiectasis (permanent scarring and enlargement of the small sacs in the lungs)
- Invasive lung disease can cause massive bleeding from the lung
- Mucus plugs in the airways
- Permanent airway blockage
- Respiratory failure
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you develop symptoms of aspergillosis or if you have a weakened immune system and develop a fever.
Prevention
Precautions should be taken when using medicines that suppress the immune system.
Related Information
AllergiesAsthma
Pulmonary tuberculosis
Aspiration pneumonia
Pulmonary aspergilloma
Invasive
Community-acquired pneumonia in adults
Blindness and vision loss
Immunodeficiency disorders
Cancer
HIV/AIDS
Chemotherapy
References
Thompson GR, Patterson TF. Aspergillus species. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 257.
Walsh TJ, Patterson TF. Aspergillosis. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 311.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 5/19/2023
Reviewed By: Jatin M. Vyas, MD, PhD, Associate Professor in Medicine, Harvard Medical School; Associate in Medicine, Division of Infectious Disease, Department of Medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2024 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
