Ewing sarcoma
Bone cancer - Ewing sarcoma; Ewing family of tumors; Primitive neuroectodermal tumors (PNET); Bone neoplasm - Ewing sarcoma; Ewing's sarcoma
Ewing sarcoma is a malignant bone tumor that forms in the bone or soft tissue around it. It affects mostly teens and young adults.
Images
I Would Like to Learn About:
Causes
Ewing sarcoma can occur anytime during childhood and young adulthood. But it usually develops during puberty, when bones are growing rapidly. It is more common in White children than in Black or Asian children.
The tumor may start anywhere in the body. Most often, it starts in the long bones of the arms and legs, the pelvis, or the chest. It can also develop in the skull or the flat bones of the trunk.
The tumor often spreads (metastasizes) to the lungs and other bones. At the time of diagnosis, spread is seen in about one third of children with Ewing sarcoma.
In rare cases, Ewing sarcoma occurs in adults.
Symptoms
There are few symptoms. The most common is pain and sometimes swelling at the site of the tumor.
Because the tumor weakens the bone, children may also break a bone at the site of the tumor after a minor injury.
Fever may also be present.
Exams and Tests
If a tumor is suspected, tests to locate the primary tumor and any spread (metastasis) often include:
- Bone scan
- Chest x-ray
- CT scan of the chest
- MRI of the tumor
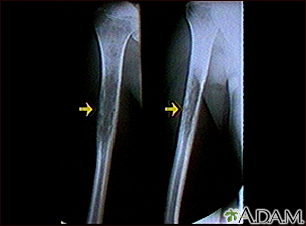
- X-ray of the tumor
A biopsy of the tumor will be done. Different tests are done on this tissue to help determine how aggressive the cancer is and what treatment may be best.
Treatment
Treatment often includes a combination of:
- Chemotherapy
- Radiation therapy
- Surgery to remove the primary tumor
Treatment depends on the following:
- Stage of the cancer
- Age and sex of the person
- Results of the tests on the biopsy sample
Support Groups
The stress of illness can be eased by joining a cancer support group. Sharing with others who have common experiences and problems can help you not feel alone.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Before treatment, outlook depends on:
- Whether the tumor has spread to distant parts of the body
- Where in the body the tumor started
- How large the tumor is when it's diagnosed
- Whether the lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) level in the blood is higher than normal
- Whether the tumor has certain gene changes
- Whether the child is younger than 15 years
- Child's sex
- Whether the child has had treatment for a different cancer before Ewing sarcoma
- Whether the tumor has just been diagnosed or has come back
The best chance for cure is with a combination of treatments that includes chemotherapy plus radiation or surgery.
Possible Complications
The treatments needed to fight this disease may have many complications. Discuss these with your health care provider.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if your child has any of the symptoms of Ewing sarcoma. An early diagnosis can increase the possibility of a favorable outcome.
Related Information
Bone tumorTumor
Long bones
Flat bones
Metastasis
References
Heck RK, Toy PC. Malignant tumors of bone. In: Azar FM, Beaty JH, eds. Campbell's Operative Orthopaedics. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 27.
National Cancer Institute website. Ewing sarcoma and undifferentiated small round cell sarcomas of bone and soft tissue treatment (PDQ) - health professional version. www.cancer.gov/types/bone/hp/ewing-treatment-pdq. Updated April 19, 2024. Accessed May 15, 2024.
National Comprehensive Cancer Network website. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology (NCCN guidelines): Bone cancer. Version 2.2024. www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/bone.pdf. Updated March 12, 2024. Accessed May 15, 2024.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 3/31/2024
Reviewed By: Todd Gersten, MD, Hematology/Oncology, Florida Cancer Specialists & Research Institute, Wellington, FL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2025 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
